Effects of melatonin on growth and antioxidant capacity of naked oat (Avena nuda L) seedlings under lead stress
- Published
- Accepted
- Received
- Academic Editor
- Mohan Lal
- Subject Areas
- Agricultural Science, Biotechnology, Plant Science, Environmental Contamination and Remediation
- Keywords
- Lead stress, Melatonin, Naked oats, Antioxidant protection
- Copyright
- © 2022 Wang et al.
- Licence
- This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed. For attribution, the original author(s), title, publication source (PeerJ) and either DOI or URL of the article must be cited.
- Cite this article
- 2022. Effects of melatonin on growth and antioxidant capacity of naked oat (Avena nuda L) seedlings under lead stress. PeerJ 10:e13978 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13978
Abstract
Melatonin (MT) plays an important role in plant response to abiotic stress. In recent years, lead (Pb) pollution has seriously affected the living environment of plants. In this study, we applied two different concentrations of MT to naked oat seedlings under Pb stress to explore the effect of MT on naked oat seedlings under Pb pollution. The results showed that Pb stress seriously inhibited the growth and development of naked oat seedlings, which was alleviated by MT. MT could increase the soluble protein content and decrease the proline content of naked oat seedlings to maintain the osmotic balance of naked oat seedlings. The application of MT could accelerate the removal of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and improve the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT), so as to maintain the redox balance in naked oat seedlings. Exogenous melatonin could significantly increase the chlorophyll content of naked oat seedlings under Pb treatment, so as to improve the photosynthesis efficiency of naked oat seedlings. MT could also remarkably up regulate the expression of the genes of LOX, POX and Asmap1, and affect the expression of transcription factors NAC and WRKY1. It might regulate the expression of downstream genes through MAPKs pathways and TFs to improve the Pb tolerance of naked oat seedlings. These results proved that MT could significantly promote the growth and development of naked oats seedlings under Pb stress, which is expected to be applied in agricultural production practice.
Introduction
After the third Industrial Revolution, science and technology made great progress; however, environmental problems also followed. The increase of motor vehicle exhaust emissions, the abuse of sewage irrigation, pesticides and chemical fertilizers, as well as the rapid development of modern mining industry have seriously polluted the soil, water and atmosphere (Pellinen, Cherkashina & Gustaytis, 2021; Zhao et al., 2015). Heavy metal contamination is potentially toxic to humans and animals, among which the heavy metal pollution problems caused by heavy metals such as lead (Pb) and mercury or their compounds, rank first for the biological threat (Rahman & Singh, 2019). Metal Pb is distributed in the atmosphere, water and soil, which leads to the excessive production and accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants through plant growth. Excessive ROS not only destroy plant proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and DNA, but also cause plant oxidative stress (Gill & Tuteja, 2010), leading to intracellular dynamic imbalance, as well as affecting and harming plant growth (Pérez-Chaca et al., 2014). At present, most plants suffer from serious Pb pollution (Pace et al., 2020). Pb could significantly reduce the leaf area and root length of Zygophyllum fabago (López-Orenes et al., 2018). Moreover, studies revealed that Pb has negative effects on the biochemical and physiological processes that regulate grain quality, and that high Pb concentrations can destroy several key metabolic processes in plants, such as organelle integrity, membrane stability, mineral metabolism, oxygen release and enzyme activities (Aslam et al., 2020). How to improve the yield and quality of crops under Pb stress and ensure food security has always been one of the popular topics in research.
Since the discovery of melatonin (MT) in plants in 1995 (Hattori et al., 1995), its function in plants has been revealed rapidly. More and more studies have found that MT plays an active role in plant stress resistance (Sun et al., 2021). MT can improve plant growth and development under drought, low temperature and salt stress conditions (Li et al., 2019; Wang, Zhang & Ding, 2020; Xia et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2020). Under heavy metal stress, MT, as an effective antioxidant (Reiter et al., 2016), can reduce the phytotoxicity of nickel by improving the efficiency of photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and the tolerance of oxidative stress of tomato seedlings (Jahan et al., 2020). MT can also reduce the toxicity of copper by improving copper fixation and scavenging ROS in cucumber (Cao et al., 2019). MT can respond to Pb stress through reducing the absorption of Pb by Carthamus tinctorius and regulating the antioxidant system of Carthamus tinctorius (Namdjoyan et al., 2020). It can reduce cadmium accumulation and reconstruct microRNA-mediated redox homeostasis to enhance plant tolerance to cadmium stress as well (Lewitt & Hulting, 2017). In addition, MT shows more other positive activities in plants, such as regulating seed germination, root growth and development, leaf senescence, circadian rhythm, postharvest fruit ripening, and plant response to adverse environmental conditions (Sun et al., 2021). It has increasingly become one of the star hormones in plant stress resistance regulation.
Naked oats are plants of the family Gramineae and oats, with the scientific name “naked grain type oats” or “naked oats”. Naked oats are native to China and recognized as one of the food crops with the highest nutritional value in the world (Zhao et al., 2020), whose protein content is the highest among cereal crops (Zhang, 2006). As a high-cold, drought-tolerant and high-quality food crop, it has lower requirements for topography (Khan et al., 2019). However, it is more vulnerable to soil pollution. It has been found that when naked oat seeds were in the heavy metal environment, the plant height, root length, and chlorophyll content were reduced (Wang, 2014). Like other crops, the growth and development of naked oats is hindered by heavy metals in the soil. But at present, the research on the metal toxicity to naked oats and the response mechanism of plants to alleviate the toxicity is still relatively insufficient. There are no data on metal toxicity mitigation and protection depending on MT in the growth of naked oats. In this paper, we have more specifically elucidated the damage caused by Pb to naked oat seedlings. For the first time, we applied different concentrations of MT and investigated the effect of different concentrations of exogenous melatonin on Pb-stressed naked oat seedlings, and demonstrated that MT can promote the growth of naked oat seedlings under Pb stress. This study shows that melatonin can be used in agricultural production.
Materials & Methods
Plant materials and seed germination conditions
The naked oat variety “Jinyan 2” (Avena nuda L.) was provided by the Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Biotechnology and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C. Healthy and full seeds were selected, disinfected for 30s with 75% alcohol, rinsed with distilled water three times, disinfected with 0.1% mercury solution for 7 min, finally rinsed with distilled water six times, moved into a water culture box containing Hoagland nutrient solution (pH 6.5 ± 0.1). Hoagland nutrient solution was replaced every three days, and the water culture box was placed in the culture room at 25 °C with 75% relative humidity, and a 14L/10D photoperiod.
Experimental group design
When the naked oats seedlings grew to the 7th day, the control group was continued to be irrigated with Hoagland nutrient solution, and the treatment group was irrigated with different concentrations of Pb solution (0, 25, 50, 75, 100 mg L−1). According to the statistical observation, the Pb treatment condition was set as 75 mg L−1 in this work. With reference to the previous experiment, the concentration of MT was selected as 50 and 100 µM (Gao et al., 2018). The experiment was divided into six treatment groups: control, Pb, MT50, MT100, MT50+Pb and MT100+Pb.Naked oat seedlings were cultured for 7 days and then treated with 0 and 75 mg L−1 Pb(NO3)2, respectively, the hydroponic solution was renewed every three days. The seedlings grown in Pb-free nutrient solution was used as the control. MT50 and MT100 were treated with MT solution of 50 and 100 µM respectively on the basis of the control group. MT50 +Pb and MT100+Pb were root-irrigated with MT solution of 50 and 100 µM on the basis of the Pb treatment group. All six treatment groups were sampled seven days after the start of stress. three groups of parallel repeats were set up for sampling, testing and measurement, respectively.
Calculation of plant height, fresh weight and dry weight
After seven days of treatment in different treatment groups, naked oat seedlings were randomly selected from each hydroponic culture box, and the plant height, plant fresh weight and plant dry weight were measured. The plant height is the linear distance from the base of the radicle to the top of the leaf. After the seedlings of naked oats were taken out, they were simply washed with tap water, then rinsed with distilled water three times, gently dried with paper towels, and the fresh plants were quickly weighed with electronic scales. The seedlings of naked oats were dried at 105 °C for 30 min, then dried at 80 °C for 24 h, and the dry weight was measured by electronic balance.
Determination of chlorophyll content and lead content
The leaf samples frozen in liquid nitrogen from -80 °C (fresh weight 0.2 g) were fully ground in liquid nitrogen with 95% anhydrous ethanol, then the volume was fixed to 20 mL, 4 °C and placed in the dark for 24 h. The values of OD649 and OD665 of supernatants were determined after samples were centrifuged for 10 min. The formula for calculating chlorophyll is as follows: C = Ca+ Cb, in which Ca =13.95A665−6.88A649−7.32A665, Cb is 24.96A649−7.32A665. Chlorophyll content = chlorophyll concentration × extraction liquid volume × dilution multiple / sample fresh weight (Porra, Thompson & Kriedemann, 1989). The content of Pb in leaves of naked oat seedlings was determined by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer (model Z2700), following the method of Shi, Li & Pan (2009). The sample was dried in an air-forced oven at 60 °C for 48 h. Dry plant material was ground in a stainless-steel blender to pass through a 0.4-mm sieve. Leaf samples were subjected to mixed acid digestion (HNO3-HClO4-HF). A certified reference material of sediment IRMM-804 with (0.42 ± 0.07) mg kg−1 Pb was purchased from the National Centre for Certificate Reference Materials, China, and was used with all patch of digestions. Dried plant samples were digested in a 4:1 (V V−1) mixture of HNO3-HClO4. Ten milliliter of mixed acids was added to 0.75 g of plant sample in a high-walled beaker and allowed to stand for 12 h at 25 °C. The samples were then heated in a sand bath at 170 °C until clear. After cooling, the solution was diluted to 25 mL with deionized water. The Pb content of the digested solutions was determined by graphite furnace AAS. A reagent blank was incorporated within each batch of analytical samples.
Determination of antioxidant enzyme activity, soluble protein and proline content
The fresh weight of the leaf sample is 0.2 g. PBS buffer (pH7.4) was added to the sample, which was ground to homogenate in an ice bath, and then centrifuged at 8,000 × g for 10 min to collect the supernatant. The supernatant was used for the determination of superoxide dismutase (SOD; EC1.15.1.1), peroxidase (POD; EC1.11.1.7) and catalase (CAT; EC1.11.1.6). The activities of SOD, POD and CAT were recorded at 550 nm, 420 nm and 405 nm, respectively, according to Elavarthi & Martin’ s method (2010).
The content of soluble proteins was detected by kits (Nanjing Institute of Bioengineering, Nanjing, China). 0.1 g of fresh leaves was homogenized with 900 µL buffer and the homogenate was centrifuged for 10 min (3000 g); 50 µL supernatant was added to three mL Coomassie brilliant blue solution. The mixture was incubated at 25 °C for 30 min and the absorbance of soluble protein content was recorded at 595 nm.
Proline content in seedlings of naked oat was measured according to the ninhydrin method described by Bates, Waldren & Teare (1973). The leaf sample was 0.2 g. Proline was extracted with 3% sulphosalicylic acid and then filtered. A portion of the filtrate was supplemented by the addition of one mL of ninhydrin and glacial acetic acid reagent. The reaction mixture was boiled (95 °C) for 1 h. Then the mixture was placed on ice to stop the reaction, the absorbance of the sample was measured at 520 nm.
Determination of malondialdehyde and ROS accumulation
Malondialdehyde (MDA) was measured according to the procedure described by Tan et al. (2019). The leaf sample (0.5 g fresh weight) was ground with five mL of 5% trichloroacetic acid and centrifuged for 10 min (8000 g, 4 °C). one mL of supernatant was mixed with one mL of 0.67% thiobarbituric acid (TBA). The mixture was then boiled in water for 30 min, the absorbance at 532 nm and 600 nm was measured respectively to calculate MDA content.
To measure H2O2, the methods described by Nawaz et al. (2018) was followed. Fresh leaves (100 mg) were ground in a mortar with 900 µL buffer, H2O2 content was recorded at a wavelength of 405 nm. The kit method (Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Biological Engineering, Nanjing, China) was applied to detect O2•−−, Fresh leaves (100 mg) were centrifuged at 4000 g and 25 °C for 10 min. 50 µL of the supernatant was mixed with the four mL reagent solution. The mixture was bathed at 37 °C for 40 min and then two mL reagent solution was added. O content was recorded at a wavelength of 550 nm.
According to the method of DAB staining (Orozco-Cardenas & Ryan, 1999), fresh leaves were soaked in DAB solution (1 mg mL−1), the pH was adjusted to 3.8, vacuum was permeated for 30 min, shaker dark treatment was placed for 8 h, washed twice with 95% anhydrous ethanol, then was boiled in a water bath (20 min), and stored in 50% glycerin after cooling, stored at 4 °C. At least three leaves were selected for each treatment, and photographed with a stereomicroscope.
Extraction of RNA and analysis of related gene expression
Sequence search and primer design were carried out according to previous work (Gao et al., 2018). The list of primers is shown in Table S1. The total RNA of naked oats was extracted by TRIzol method. First-strand cDNA was synthesized using the PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit with the gDNA Eraser (Takara, Shiga, Japan). qRT-PCR was performed on a Bio-Rad CFX96 Real-Time PCR System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) using FastStart Essential DNA Green Master (Tiangen, Beijing, China). The procedure is as follows: 95 °C for 10 min, 1 cycle, 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 40 cycles. Finally, a melting curve was drawn to reconfirm the specificity of the primers by heating the product from 60 °C to 95 °C. The internal reference gene was Actin (KP257585.1) (Gao et al., 2018; Genty, Briantais & Baker, 1989). Three independent biological replications were performed for each experiment. The relative gene expression levels were calculated according to the 2−ΔΔCt method and presented as fold changes.
Data analysis
All the measurements reported in this study are the means of three replicates. Vertical bars represent ± S.D. SPSS26.0 software was used for data statistics univariate analysis and minimum significant difference (LSD) test to compare the average values. We use prism 8.00 to organize pictures.
Results
MT improves the growth of naked oat seedlings under lead stress
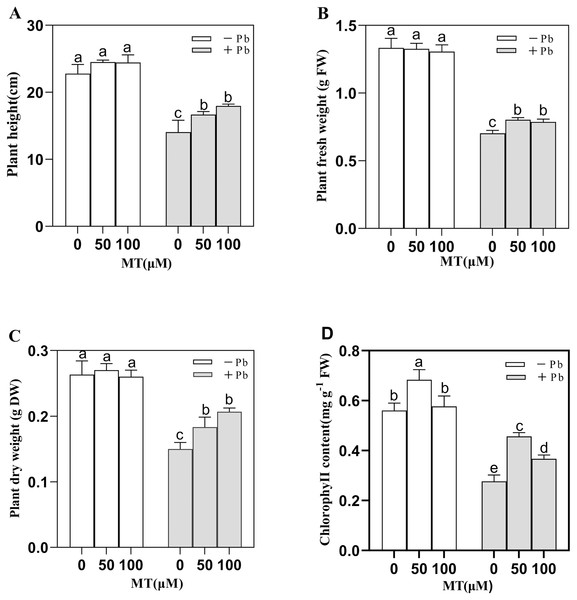
In the simulated experimental group (Control, Pb, MT50, MT100, MT50 +Pb, MT100 +Pb), on the 7th day (Fig. 1), the Pb solution decreased the plant height, fresh weight, dry weight and total chlorophyll content of naked oat seedlings. Under Pb stress, MT treatment improved seedlings growth with the plant height of seedlings increasing by 27.8% in MT100 +Pb group, and 18.6% in MT50 +Pb group compared with Pb group (Fig. 1A). The fresh weight of seedlings decreased by 47.2% after Pb treatment, which was significantly alleviated by the application of MT (Fig. 1B). Compared with the the Pb group, the dry weight of MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups increased by 20% and 33.3%, respectively (Fig. 1C). The chlorophyll content of the seedlings treated with 50 and 100 µM MT increased by 21.4% and 1.7% respectively compared with the control group, and the effect of 50 µM MT was more significant. Pb stress decreased the total chlorophyll content, but after MT treatment, the total chlorophyll content of naked oat seedlings increased considerably, with leaves also turning to green. Furthermore, the toxic symptoms were alleviated, with the total chlorophyll content increasing by 66.7% and 33.3% respectively compared with the Pb group. It can be observed that Pb inhibited the growth of naked oat seedlings, while the application of exogenous MT improved the tolerance of naked oat seedlings to Pb.
Figure 1: Effects of different concentrations of MT on the growth of naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
(A) Plant height; (B) plant fresh weight; (C) plant dry weight; (D) chlorophyll content. − Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, + Pb means 75 mg L−1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P < 0.05).Exogenous application of MT enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes in naked oat seedling cells
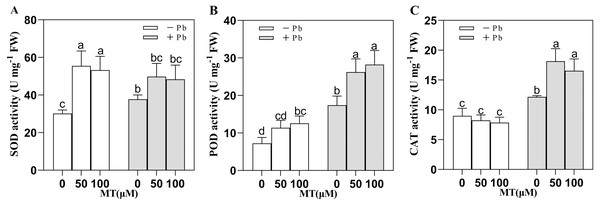
SOD, POD and CAT are important protective enzymes in plants, and they are all important indicators of plant resistance to stress. Pb stress changed the antioxidant enzyme activity of naked oat seedlings (Fig. 2), in which SOD, POD, CAT activity increased. After 50 and 100 µM MT pretreatment, SOD activity was significantly increased by 84.0% and 76.4%, respectively. Interestingly, the efficiency of MT to increase SOD activity decreased under Pb stress, but after MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb treatment, it increased 31.8% and 28.1% respectively compared with Pb group. Compared with the Pb stress group, the POD activity of the group treated with MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb increased by 50.7% and 62.0%, while the activity of CAT increased by 49.5% and 36.0%. The results showed that exogenous MT could enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes in naked oats cells under Pb stress, so as to strengthen the antioxidant system of plants and reduce the toxicity of Pb to naked oats.
Figure 2: Effect of MT treatment on enzyme activity of naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
(A) SOD; (B) POD; (C) CAT. − Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, + Pb means 75 mg L−1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P < 0.05).Changes of osmotic regulation substances in naked oat seedlings
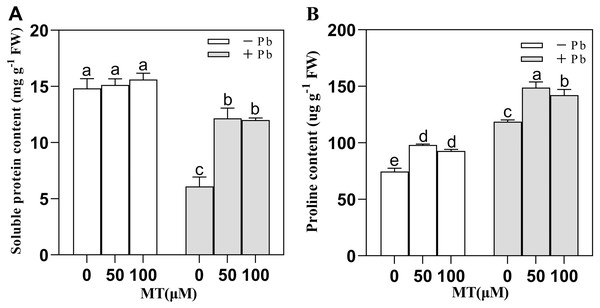
After naked oat seedlings cells sensed the external Pb stress, plant soluble proteins and proline increased or decreased accordingly to maintain the redox balance and alleviate the Pb poisoning of plant cells (Fig. 3). MT50 and MT100 treatment did not cause significant changes in intracellular soluble protein content in the control group, and Pb stress decreased the soluble protein content, but after 50 µM or 100 µM MT pretreatment, the soluble protein content increased. Compared with the Pb group, the soluble protein content of MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb group increased by 99.3% and 96.9%, respectively (Fig. 3A). The content of proline increased by 31.5% and 24.2% in MT50 and MT100 treatments, respectively compared with the control group (Fig. 3B). Pb stress significantly increased proline content, and the effect of MT treatment was more significant. In MT50 +Pb treatment group it increased by 25.4% while for MT100 +Pb group the number was 19.8%. Therefore, MT might eliminate the increase of ROS in naked oat seedlings caused by Pb stress, stabilize the molecular structure of soluble proteins and enhance the tolerance of naked oats to heavy metal Pb stress. At the same time, the ROS of naked oat seedlings were elevated under Pb stress, and MT application could effectively alleviate the accumulation of ROS in naked oat seedlings.
Figure 3: Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on osmotic regulatory substances in naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
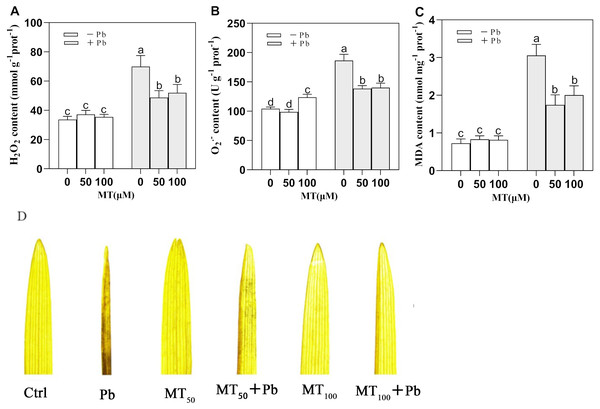
(A) soluble protein content; (B) proline content. − Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, + Pb means 75 mg L−1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P < 0.05).Pb stress caused a significant increase in the contents of H2O2 and O in young leaves of naked oats (Fig. 4). MT could significantly alleviate this phenomenon. Compared with the Pb group, the contents of H2O2 in MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups decreased by 30.3% and 25.7%, respectively, and the content of O decreased by 25.7% and 24.7%, respectively. In the experiment, the content of MDA increased significantly under Pb stress, but MT treatment could reduce the content of MDA, and the content of MDA decreased by 42.9% and 34.4% in MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups, respectively (Fig. 4C). DAB histochemical staining of naked oat seedling leaves (Fig. 4D) showed that Pb stress induced oxidative stress of naked oats, and a large amount of H2O2 was accumulated in seedling leaves, which affected the leaf morphology. After Pb poisoning, the seedling leaves became smaller and narrower, and the DAB staining was aggravated. After MT treatment, the symptoms of the leaves treated with MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb were relieved, and the accumulation of H2O2 was reduced. The above results showed that after the Pb ion entered into naked oat seedlings, oxidative stress produced O2•−, H2O2 and other reactive oxygen species, which could be reduced by external application of MT. It is speculated that MT might be used as an antioxidant to help plants remove excessive ROS, lessen the degree of membrane lipid peroxidation in naked oat leaves, improve their tolerance under Pb stress, and improve the growth of naked oat seedlings.
Figure 4: Effects of different concentrations of MT on the changes of intracellular reactive oxygen species in naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
(A) H2O2 content; (B) O content; (C) MDA content; (D) DAB staining histochemical analysis. − Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, + Pb means 75 mg L−1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P < 0.05).Exogenous MT application increases the expression of genes related to oat seedlings
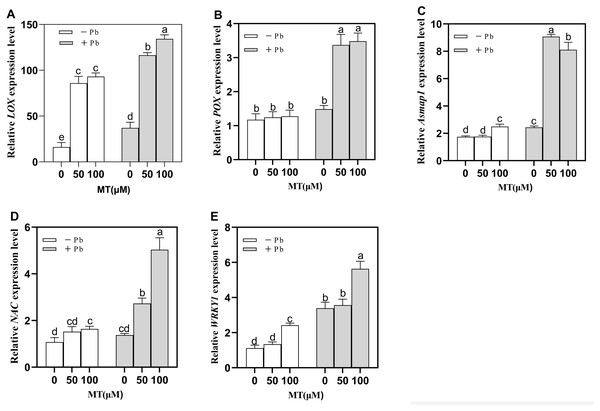
The expression of Lipoxygenase (LOX) and peroxygenase (POX) of naked oats changed significantly after exogenous application of MT (Figs. 5A and 5B). A total of 50 and 100 µM MT significantly increased the expression of LOX by 431.2% and 475.5%. Under Pb stress, the expression of LOX in MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups was also significantly increased by 214.3% and 262.3% (Fig. 5A). POX gene expression also increased significantly after Pb stress, and exogenous MT pretreatment increased 127.7% and 135.1% respectively (Fig. 5B). The results showed that MT treatment changed the expression level of lipid peroxidase in naked oat cells under Pb stress, which may protect plants from oxidative stress by up-regulating LOX and POX.
Figure 5: Effects of different concentrations of MT on the expression of LOX (A), POX (B), Asmap1 (C), NAC (D), WRKY1 (E) in leaves of naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
− Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, + Pb means 75 mg L−1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P < 0.05).Asmap1 gene is a MAPK (mitogen activated protein kinase) protein in naked oats. After MT pretreatment, there was no significant change in MAPK cascade response in the Control group, after Pb treatment, Asmap1 gene expression increased significantly by 273.3% and 233.7% respectively (Fig. 5C) in MT50+Pb and MT100+Pb groups treated with MT, indicating that MT50 can induce a stronger MAPK cascade response. It is suggested that MT can induce gene upregulation in MAPK cascade reaction and enhance the tolerance of naked oat seedlings to Pb stress.
Compared to the Pb group (Fig. 5D), the gene (NAC) expression of MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups increased significantly by 99.1% and 267.2% respectively. Compared to the Pb group, the gene (WRKY1) expression of MT50 +Pb and MT100 +Pb groups increased by 5.0% and 66.1%. It is speculated that exogenous MT may affect the expression of related TFs in naked oat seedlings in some way, and further enhance the tolerance of naked oat seedlings to Pb stress.
Discussion
MT can reduce the oxidative stress damage caused by heavy metals in some plants (Sarafi et al., 2017). The differences of its concentration and treatment methods, stress, as well as environments have distinctive effects on the same plant. The Pb tolerance of plants is the result of synergistic function in plants, and one of the indicators is plant biomass (Liu, Li & Shen, 2007). Under 75 mg L−1 Pb stress, the plant height, fresh weight and dry weight of naked oats seedlings were reduced, the growth slowed down, and serious wilting appeared. After exogenous MT pretreatment, the wilting growth state of naked oats seedlings was effectively alleviated and gradually returned to normal, this is similar to Hasan et al. (2015).
Photosynthesis maintains plant growth and development, and the change of chlorophyll content in chloroplast can be used as a marker to measure photosynthetic efficiency (Lee et al., 2003; Xiong, Zhao & Li, 2006). In our experiment, Pb stress led to the decrease of chlorophyll content which could be increased by MT treatment in varying degrees. Chlorophyll content is closely related to the dry weight of the plant (Hu et al., 2018), the increase of chlorophyll content may also increase the dry weight of naked oat seedlings. So we speculated that MT could improve the photosynthetic efficiency and help the seedlings to restore growth.
Singh et al. (2010) found that under the stress of heavy metal Pb, a large amount of ROS in indica rice cells could accumulate and destroy the balance in the oxidation system and aggravate membrane lipid peroxidation. The activities of SOD, POD and CAT in naked oats seedlings induced by Pb stress did not change significantly, while exogenous MT increased the activities of the three. The increase of activity was related to the concentration of MT, in which POD and CAT changed significantly, while SOD activity was not sensitive to Pb. Overall, MT application enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes, which is similar to the findings of Xia et al. (2020). At the same time, metal Pb caused a large accumulation of ROS and a significant increase of H2O2 and O in naked oat cells, and MT could effectively alleviate this phenomenon, lessen the oxidative damage of young leaves (Fig. 5), and help naked oat seedlings to resist the toxicity of metal Pb.
Heavy metals can damage intracellular soluble proteins (Yadav, 2010). 75 mg L−1 Pb stress significantly decreased the content of soluble proteins in naked oat seedlings while MT treatment increased it. It is speculated that MT as an active oxygen scavenger maintains intracellular homeostasis and alleviates metal-induced protein damage, which is consistent with the discovery by Namdjoyan et al. (2020). Free proline in plant osmotic regulators increases under stress, which helps to alleviate the toxic effects caused by abiotic stress and protect plant cells from the harm of free radicals (Soussana et al., 2004). The proline content of young leaves of naked oats treated with Pb was higher than that of the control group, which may be because the infiltration of metal Pb ions induced the change of water potential in the seedlings and destroyed the equilibrium state. MT under Pb stress can increase the content of proline, and proline can regulate cell osmotic pressure (Lehmann et al., 2010). It may regulate cell osmotic pressure balance and enhance the tolerance of naked oats to Pb by clearing excess ROS in cells. The content of MDA, the product of membrane lipid peroxidation, indirectly reflects the degree of damage to the membrane system (Atalay, Gegotek & Skrzydlewska, 2021). This study showed that the application of melatonin significantly reduced MDA levels, further demonstrating that melatonin can maintain osmotic balance in naked oat seedlings. In conclusion, the exogenous application of melatonin maintained the osmotic balance of naked oat seedlings, and we speculate that the increase in fresh weight of naked oat seedlings may be related to this.
Usually, H2O2, as a signal molecule with low concentration, participates in a variety of physiological and metabolic regulation in plants (Nazir, Fariduddin & Khan, 2020) and regulates the expression of transcription factors in bacteria, animals and lower eukaryotes (Marinho et al., 2014). Exogenous application of melatonin can significantly reduce the H2O2 content in naked oat seedlings. We speculate that MT may promote the expression of stress resistance genes by reducing the H2O2 concentration. MAPK cascade reaction is a common cascade reaction in abiotic stress (Wang, He & Yang, 2012). Asmap1 is an important gene in MAPK. We found that Asmap1 was significantly up-regulated after melatonin was applied. Therefore, MT may enhance plant Pb tolerance by affecting MAPK pathway. Transcription factor (TFs) regulates the expression of coding genes, especially the expression of early stress response genes and a series of downstream target genes, which may enhance plant stress resistance (Hoang et al., 2017). Genes such as NAC and WRKY are involved in a variety of abiotic stress responses, and the overexpression of NAC and WRKY genes can regulate the senescence process of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves (Guo, Cai & Gan, 2004). In this study, exogenous MT significantly increased the expression of NAC and WRKY1. MT may also promote the growth of naked oat seedlings under Pb stress by affecting the expression of TFs. In general, MT may affect the MAPK cascade and the expression of TFs, thus improving the Pb tolerance of naked oat seedlings.
LOX and POX genes in plants are involved in a variety of signal pathways (Santino et al., 2013), helping the body resist adverse external factors. Under salt stress, the activity of lipoxygenase in the cells of citrus seedlings increased (Ben-Hayyim et al., 2001), and the 9-LOX gene expression increased three to six times under osmotic stress (Fedina et al., 2004). Similarly, naked oat seedlings in this study showed slightly elevated expression levels of LOX and POX under Pb stress. LOX may help activate antioxidant enzyme system (Cho et al., 2012), The expression levels of LOX and POX were significantly increased in naked oat seedlings after exogenous application of different concentrations of MT, and we speculate that exogenous MT may enhance the resistance of oat seedlings by regulating the expression levels of LOX and POX. This is similar to the results of the study by Gao et al. (2018).
This study provides the first evidence that MT may help to alleviate the damage suffered by naked oat seedlings under Pb stress. In some areas, crops are experiencing heavy metal contamination (Onakpa, Njan & Kalu, 2018), especially in acidic soils, which tend to accumulate more heavy metals. It is urgent to reduce the negative impact of heavy metals in soils on crops. On the one hand, MT can alleviate heavy metal toxicity in plants, while at the same time improve soil enzyme activity and soil quality by altering the composition of soil bacterial and fungal communities, thereby promoting plant growth (Acuña Castroviejo et al., 2014; Li et al., 2018; Madigan et al., 2019; Moustafa-Farag et al., 2020). On the other hand, MT may also alleviate abiotic stresses to which plants are subjected in other ways (Chang et al., 2021), such as by affecting circadian rhythms. Soil Pb concentrations in some vegetable gardens were much higher than those in this experiment (Amorim et al., 2021), and the therapeutic effect of MT remained stable in the short term (Yan et al., 2021). In summary, MT has the potential to be applied in future agricultural practices as one of the substances to improve the growing environment of crops such as naked oats.
Conclusions
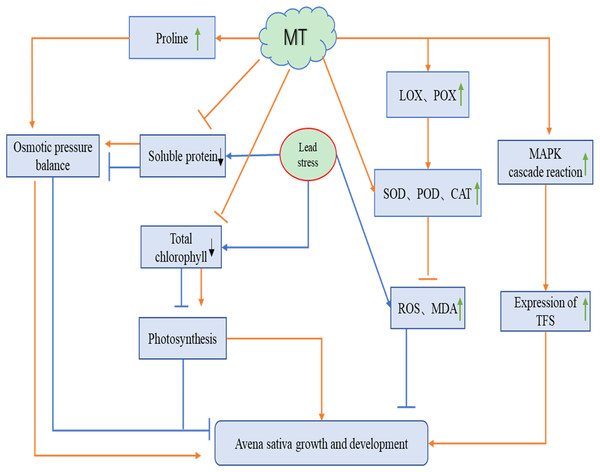
A total of 75 mg L−1 Pb stress severely affected the growth of naked oat seedlings, while different concentrations of MT all alleviated the damage caused by Pb stress to oat. We speculated that MT may act on naked oat seedlings under Pb stress in the following ways (Fig. 6): exogenous MT can increase chlorophyll content and enhance photosynthesis in oat seedlings. It can also promote changes in osmoregulatory substances such as proline to restore the growth and development of Pb-stressed naked oat seedlings. Pb stress significantly increased the level of reactive oxygen species in oat seedlings, while exogenous MT was able to significantly reduce the level of reactive oxygen species in oat seedlings by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Exogenous MT up-regulated the expression of genes related to the antioxidant system, activated the MAPK cascade reaction and promoted the expression of TFs genes, thus improving the resistance of naked oat seedlings to Pb. The relationship between the mechanism of the function of MT and related signaling pathways in naked oat seedlings under heavy metal Pb stress needs to be further explored.
Figure 6: Potential role of MT on the growth and development of naked oat seedlings under lead stress.
The orange line indicates the pathway of action for melatonin (MT) and the blue line indicates the pathway of action for lead stress. Green arrows indicate an increase, black arrows indicate a decrease.Supplemental Information
The growth phenotype of oat seedlings under the different concentration of lead in culture solution
7-day-old seedlings were treated with different concentration lead solution for 7 days (0–100 mg L-1). Scar bar represent 5 cm.
Changes in lead content in leaves following exogenous application of melatonin
Pb means lead-free and it is not a stress, Pb means 75 mg L-1 lead stress. Data are shown as means ± SD (n=3). Alphabets indicate a significant difference between control and treatment (P ¡ 0.05).