Experience of COVID-19 disease and fear of the SARS-CoV-2 virus among Polish students
Author and article information
Abstract
Background
The SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic has significantly affected individuals and entire societies. It has caused a number of adverse consequences for public health. It has contributed to lower average life expectancy and significantly reduced the sense of health security. It has affected not only physical but also mental health. COVID-19 infections have become so common in many countries, including Poland, that almost every member of society has either experienced it themselves or has a family member or friend who have been affected by the disease. The investigations undertaken in the article concern the fear of COVID-19 infection among Polish university students, determined by the experience of the disease –whether direct or among loved ones.
Methods
An online survey was conducted with 851 students. It took place between 1 and 15 March 2021, a year after detection of the first case of infection with the virus in Poland. The aim of the study was to find out about the relationship between the experience of COVID-19 disease (whether direct or among people close to the respondent) and fear of this disease among university students in Poland. The analysis used intergroup comparison tests (Mann–Whitney U Test and t-test).
Results
The results indicate that the level of fear of COVID-19 among Polish university students was low (M = 1.98; SD = .49), with women (M = 2.04; SD = .75) presenting statistically higher (t (620.46) = 3.05; p = .002) fear than men (M = 1.87; SD = .74). The situation of the respondent having had a close person fall ill with COVID-19 or die as a result of coronavirus infection was found to be significant for the level of experienced fear of COVID-19 in the studied group (t (469.46) = −2.98; p = .003).
Conclusions
The significantly higher level of fear in the group of young people who knew someone close with severe (fatal) COVID-19 disease indicates that psychological support may be more significant for such people than for individuals who have not experienced such a situation. A similar conclusion can be formulated taking into account the gender criterion, as the results make it possible to predict that women expect more support in a pandemic situation.
Cite this as
2022. Experience of COVID-19 disease and fear of the SARS-CoV-2 virus among Polish students. PeerJ 10:e14356 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14356Main article text
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic forced people around the world to face previously unknown challenges. COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. One of the characteristic features of any infectious disease is fear. It is significantly linked to the manner of perceiving difficult situations, to the undertaking of certain behaviors, and to adaptation processes. Fear is a natural reaction of the body indicating potential danger, and mobilizing the individual to take actions to cope (Lazarus, 1986; Borecka-Biernat, 2017).
Studies related to COVID-19 have confirmed increased levels of fear around the world (Knipe et al., 2020). The most common causes of fear which are emphasized include fear of accidental contact with an infected person, fear of being infected or of infecting one’s nearest and dearest, and the fear of isolation from other people (Lin, 2020). Fear of the infectious disease is mainly associated with the rapidity of the spread of the virus, the high risk of infection, and the substantial mortality rate (Pappas et al., 2009).
It has been proven that during a pandemic, a certain level of fear has a significant positive effect on protective behaviors, is an important predictor of observance of social distancing and hand hygiene rules, and plays an important role in adherence to measures protecting against infection (Pakpour & Griffiths, 2020; Harper et al., 2021). However, increased fear can lead to panic and misinterpretation of insignificant complaints as symptoms of the disease (Asmundson & Taylor, 2020), it becomes one of the major factors increasing the level of stress, and exacerbating existing mental health problems (Colizzi et al., 2020).
Researchers have pointed out that the level of fear experienced depends on many factors, including, among others, the individual’s own resources (Eysenck, MacLeod & Mathews, 1987), the social support network (Cohen & McKay, 1984), as well as gender and age. Numerous studies show that, in general, women are more fearful and develop anxiety disorders more often than men (Cameron & Hill, 1989; Brody, Lovas & Hay, 1995; Gallacher & Klieger, 1995; Kelly et al., 2008; McLean & Anderson, 2009; Hallers-Haalboom et al., 2020). Higher levels of fear in women concern both open and hidden fear, although it is worth noting that gender differences in implicit measures were found to be approximately half the size of those in explicit measures (Egloff & Schmukle, 2004).
The COVID-19 pandemic also proved to be a greater trauma and cause of stress for women than for men, even though men appeared to be a group more vulnerable to adverse health consequences associated with the coronavirus (Fitzpatrick, Harris & Drawve, 2020; Giordani et al., 2020; Tzur Bitan et al., 2020; Islam et al., 2020; Bonnici, Clark & Azzopardi, 2020; Niño et al., 2021; Alsyouf et al., 2021; Sari et al., 2021; Sánchez-Teruel et al., 2022; Broche-Pérez et al., 2022). Other researchers also pointed out that fear of COVID-19 significantly reduced women’s mental health during the pandemic (Guadagni, Umilta’ & Iaria, 2020; Ahmed et al., 2020; Salehi et al., 2020; Casagrande et al., 2020; García-Fernández et al., 2021; Siddique, Ahmed & Hossain, 2021; Khattak et al., 2021).
The level of fear of COVID-19 infection also varies across age groups. It seems to be relatively lower in young people compared to older people (Długosz, 2020; Saravanan et al., 2020; CBOS, 2021). However, even though younger people are at a lower risk of both severe COVID-19 and complications of the disease (Colizzi et al., 2020), they also experience a number of negative consequences of the pandemic. Young people suffer mainly due to social distancing and self-isolation caused by lockdowns. The limitations concerning physical, social, and economic activity are among the main causes of anxiety and depression experienced particularly by health professionals, by older people, but also by younger people, including students (Zhang et al., 2020; Sahu, 2020; Cao et al., 2020; Odriozola-González et al., 2020; Ballester et al., 2020; Roy & Covelli, 2020; Bolatov et al., 2020).
The results of studies conducted on groups of students have shown that during the pandemic they have been experiencing increased levels of stress, anxiety and fear for their own health and that of their loved ones, problems focusing, sleep disturbances, increased concerns about academic performance, and severe consequences of reduced social interactions (Son et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Köktürk Dalcalı, Durgun & Taş, 2021). The pandemic has also had a negative impact on their mental health (Chirikov et al., 2020; Morales-Rodríguez, 2021; Marques et al., 2021). Experiencing symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress has affected students’ life satisfaction, psychological well-being, and adaptive coping (Lopes & Nihei, 2021). A significant difference was also found concerning fear related to COVID-19 depending on the students’ gender, with women reporting higher levels of fear on average compared to men (Rodríguez-Hidalgo et al., 2020; Zolotov et al., 2022).
Researchers have pointed out that the likelihood of anxiety and depression symptoms is significantly higher if the individual knows someone who has suffered (or is suffering from) COVID-19 (Ma et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2020; Mertens et al., 2020; Son et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Elsharkawy & Abdelaziz, 2021; Bourion-Bédès et al., 2021; Vigo et al., 2021; Green et al., 2021).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, fear and anxiety, associated with the threats resulting from the epidemic situation, was defined by Ahorsu et al. (2020) as fear of COVID-19. This construct was used in the present study, expecting that one’s own experience of contracting COVID-19, the experience of a loved one contracting the disease, and the latter’s severity, would significantly differentiate the level of experienced fear of COVID-19.
On this basis, we formulated the following hypotheses: Hypothesis 1: Women declared a higher level of fear of COVID-19 than men. Hypothesis 2: Individuals who have had COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones who have not had it. Hypothesis 3: Individuals knowing a close person who fell ill with COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones not knowing anyone close who fell ill with COVID-19. Hypothesis 4: Individuals knowing a close person who became severely ill with or died of COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones knowing someone close who was asymptomatic/lightly ill with COVID-19.
Our additional aim was to find out the specificity of fear of COVID-19 (its level and structure) in a group of young people, students of Polish universities.
Materials & Methods
Participants
Written approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Silesia to conduct the study (number of the approval: KEUS.95/02.2021). The research was conducted between 1 and 15 March 2021. It was performed by Biostat, a professional data collection and online survey company. Participation in the study was voluntary. All participants gave informed written consent to participate. They were apprised of the possibility of withdrawing from the study without giving any reason. Participants were also informed that their responses would be used only for research purposes and that researchers would not receive any personal information about study participants. A total of 851 respondents took part in the survey, including 552 women and 299 men. University students from all over Poland were included in the study. The mean age was M = 21.36 (for women: M = 21.41, for men: M = 21.26). Only a slight majority of the respondents: 51.4% (N = 437) were only students at the time of the survey, while the remaining 48.6% (N = 414) were studying and working.
Measures
The tool used included the Fear of COVID-19 scale (Ahorsu et al., 2020), personal data (e.g., age: between 19 and 24, gender: woman, man), and additional questions formulated to verify the research hypotheses:
Have you had COVID-19? (yes, no).
If yes, what is/was the disease like? (asymptomatic, light, severe, very severe).
Has any of your relatives or friends been ill with COVID-19? (yes, no).
If yes, what is/was the disease like? (asymptomatic, light, severe , very severe, fatal).
The Fear of COVID-19 scale (FCV-19S) is a unidimensional scale measuring the level of fear of COVID-19. It consists of seven items rated on a five-point scale from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 5 (“strongly agree”). The total score is calculated by adding up all the items. Higher scores indicate higher levels of fear of COVID-19. The studies used the Polish adaptation of the scale by Pilch, Kurasz & Turska-Kawa (2021). The authors have permission to use this instrument from the copyright holders. In addition, the toolkit included questions aimed at identifying the experience of the illness by the respondents and their loved ones. The research also concerned the severity of the disease among the individuals (asymptomatic/light or severe/fatal).
The IBM SPSS software (version 26) was used to compute statistical analyses.
Results
In the beginning, descriptive statistics for the FCV-19S scale (mean, standard deviation) were checked, as well as the reliability coefficients given in Table 1.
| Variables | Reliability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | α | ω | Avg. interitem correlation | Avg. item-rest correlation | |
| Fear of COVID-19 | 1.98 | 0.49 | .86 | .86 | .48 | .63 |
Reliability indices for the Fear of COVID-19 scale are satisfactory, with α = .86 95% CI [.84–.87], ω = .86.
The remaining analyses were based on group comparisons. The independent t-test and the Mann–Whitney test were used depending on the assumptions met for individual tests. Details on these analyses are provided later on in the article.
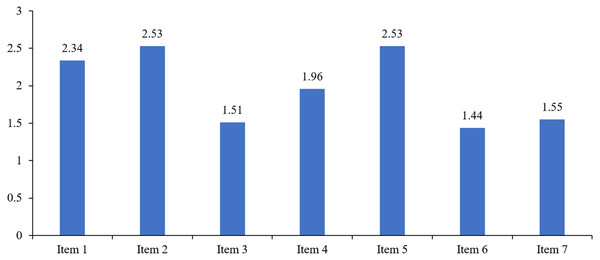
Table 2 presents descriptive statistics for the individual items of the Fear of COVID-19 scale:
| Items | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.34 | 1.07 |
| 2 | 2.53 | 1.20 |
| 3 | 1.51 | 0.79 |
| 4 | 1.96 | 1.10 |
| 5 | 2.53 | 1.25 |
| 6 | 1.44 | 0.80 |
| 7 | 1.55 | 0.87 |
-
I am most afraid of coronavirus-19.
-
It makes me uncomfortable to think about coronavirus-19.
-
My hands become clammy when I think about coronavirus-19.
-
I am afraid of losing my life because of coronavirus-19.
-
When watching news and stories about coronavirus-19 on social media, I become nervous or anxious.
-
I cannot sleep because I’m worrying about getting coronavirus-19.
-
My heart races or palpitates when I think about getting coronavirus-19.
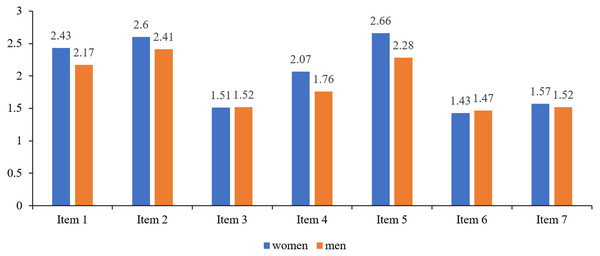
Figure 1 presents the Fear of COVID-19 structure in the studied group. Table 3 and Fig. 2 present the structure of fear of COVID-19 for the individual items by gender.
Figure 1: Fear of COVID-19 structure in the studied group.
Hypothesis 1: First, the difference between the genders in terms of perceived fear of COVID-19 was checked. The assumption of normality was not met in either group (for women, W = .95; p < .001; for men W = .93; p < .001), therefore the bootstrap for independent samples test was used (Field, 2013). The analyses showed that fear of COVID-19 was significantly higher in young women (N = 552) than in young men (N = 229). The results are presented in Table 4.
Figure 2: Fear of COVID-19 structure taking into account the gender criterion.
| Items | Women | Men | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| 1 | 2.43 | 1.09 | 2.17 | 1.02 |
| 2 | 2.60 | 1.19 | 2.41 | 1.19 |
| 3 | 1.51 | 0.76 | 1.52 | 0.84 |
| 4 | 2.07 | 1.15 | 1.76 | 0.98 |
| 5 | 2.66 | 1.23 | 2.28 | 1.25 |
| 6 | 1.43 | 0.78 | 1.47 | 0.83 |
| 7 | 1.57 | 0.89 | 1.52 | 0.84 |
| Variables | Women | Men | t(620,46) | p | Cohen’sd | MeanDifference | 96% Confidence Interval of the Differencea | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Fear of COVID-19 | 2.04 | 0.75 | 1.87 | 0.74 | 3.05 | .002 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.26 | |
Notes:
Fear of COVID-19 in the female group was M = 2.04, 95% CI [1.97–2.10], SD = .75, while in the male group it was M = 1.87, 95% CI [1.79–1.96], SD = .74. This difference = .16, BCa 95% CI [.06–.26] was statistically significant, t (620.46) = 3.05, p = .002.
Hypothesis 2: Individuals who have had COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones who were not infected did not fall ill with COVID-19 (Table 5).
| Independent-samples Mann–Whitney U test summary | |
|---|---|
| Total N | 851 |
| Mann–Whitney U | 30,487.50 |
| Standard Error | 2,188.40 |
| Standardized Test Statistic | −1.56 |
| Asymptotic Sig. (2-sided test) | .12 |
Due to the unequal sample size in the two groups, as well as to the failure to meet the normality assumption (individuals who have been ill with COVID-19 W = .92; p < .001; individuals who have not been ill with COVID-19 W = .95; p < .001), the Mann–Whitney test was used.
The level of fear of COVID-19 in the group of individuals who have had COVID-19 (N = 89) was not significantly different from that in the group of individuals who have not had it (N = 762), U = 30487.5; z = − 1.56; p = .12; r = − .05.
Hypothesis 2 was not confirmed.
Hypothesis 3. Individuals knowing someone close who fell ill with COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones who did not know anyone close to them ill with COVID-19.
Initially, the assumption of normality was checked, which was not met for either group (individuals who know someone close who fell ill N = 538; W = .94; p < .001; individuals who do not know someone close who fell ill N = 313; W = .94; p < .001). Therefore, the bootstrap for independent samples test was used. The results are presented in Table 6.
| Variables | Close person had COVID-19 | No close person had COVID-19 | t(647.308) | p | Cohen’sd | MeanDifference | 96% Confidence interval of the differencea | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Lower | Upper | |||||
| Fear of COVID-19 | 2.01 | 0.75 | 1.94 | 0.76 | 1.33 | .19 | 0.09 | 0.07 | −0.04 | 0.16 |
Notes:
The level of fear of COVID-19 in the group of individuals who knew someone close to them had had COVID-19 was M = 2.01, 95% CI [1.94, 2.07], SD = .75, while in the group of those who did not know anyone close who had been ill, level of fear was M = 1.94, 95% CI [1.85–2.02], SD = .76. This difference = .07, BCa 95% CI [−.04–16] was statistically insignificant, t (647.308) = 1.33, p = .19.
Hypothesis 3 was not confirmed.
Hypothesis 4: Individuals knowing a close person who became severely ill with or died of COVID-19 will present higher levels of fear of the coronavirus compared to ones knowing someone close who was asymptomatic/lightly ill with COVID-19.
In the last analysis, two groups were distinguished based on the severity of the disease in the respondents’ environment. The first group included respondents who knew a close person with an asymptomatic or light course of the disease, N = 311, and the second group included those who knew a close person with a severe or fatal course N = 227. In both groups the assumption of normal distribution was not met (asymptomatic/light group W = .93; p < .001; severe/fatal group W = .96; p < .001). Therefore, as in the previous analyses, it was decided to use the bootstrap for the independent samples test. Table 7 presents the differences between individuals who knew a close person with asymptomatic/light or severe/fatal course of the disease in terms of fear of COVID-19.
| Variables | Asymptomatic/Light | Severe/Fatal | t(469.46) | p | Cohen’sd | MeanDifference | 96% Confidence interval of the differencea | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Fear of COVID-19 | 1.92 | 0.72 | 2.12 | 0.77 | −2.98 | .003 | −0.26 | −0.20 | −0.33 | −0.08 | |
Notes:
Fear of COVID-19 in the group of people who knew someone close to them with an asymptomatic/light course of the disease (N = 331) was M = 1.92, 95% CI [1.84–2.00], SD = .72, while in the group of respondents who knew someone close to them with a severe/fatal course (N = 227), it was M = 2.12, 95% CI [2.02–2.22], SD = .77. This difference, = .20, BCa 95% CI [.33–.08] was statistically significant, t (469.46) = −2.98, p = .003.
Discussion
Knowledge about the determinants, specificities and consequences of fear of COVID-19 is extremely important and valuable. It makes it possible to develop and implement specific actions and programs, including in the field of public health, to mitigate the psychosocial and health-related effects of the pandemic. The core element of the study presented in this article was to determine the associations between one’s direct experience of falling ill with the disease or knowing a close person who was ill, and fear of COVID-19.
The present study partly confirmed the results of other studies, according to which fear would occur much more often among those who knew someone who had suffered or who was suffering from COVID-19. However, in the case of Polish students, higher levels of fear were found only among those who knew someone with a severe/fatal course of the disease. The mere fact that someone in the students’ closest circle had been ill with the coronavirus did not mean that they had higher levels of fear of COVID-19 compared to those who did not know anyone who had suffered from the disease. This may indicate a certain lack of fear related to the potential possibility of infection and severe COVID-19. In relation to Poland, this may have been one of the effects of the narrative pursued especially in the early phases of the pandemic, according to which young and healthy people did not constitute risk groups for severe or fatal disease. This may also have been influenced by the fact that asymptomatic or oligosymptomatic COVID-19 was actually much more frequent there than in the older group. According to the results of the present study, individuals who had had the disease did not generally present a higher fear of coronavirus than ones who had not had COVID-19, which may be linked precisely to the light course of the disease.
The study further showed that the level of fear declared by students in Poland (mean age for women M = 21.41, for men M = 21.26) was low (Pilch, Kurasz & Turska-Kawa, 2021) with higher levels of fear linked to the mental, cognitive domain (thinking about the coronavirus, experiencing general anxiety caused by the coronavirus, including fear of loss of life, watching news about the coronavirus) rather than to the somatic domain (palms sweating, sleep problems, heart racing). This is consistent with findings from other studies, indicating that young people have lower fear of COVID-19 compared to people in older age groups (Długosz, 2020; Saravanan et al., 2020; CBOS, 2021). At the same time, however, as proven by the review and meta-analysis of the studies on fear of COVID-19 among college students conducted in 11 countries, the level of that fear which they reported was moderate. Thus, Polish students differed in terms of presented fear of COVID-19 from their younger counterparts (Wang et al., 2022).
It was also found on the basis of the results that the level of fear of COVID-19 was significantly higher in female students than in male students. A fear structure analysis taking into account the gender criterion leads to the conclusion that in women, the level of fear of COVID-19 manifested in the mental domain is higher than in men, while in the somatic domain, gender does not differentiate the level of experienced anxiety.
It is particularly important to note, in line with the findings of the studies analyzed here, that during the COVID-19 pandemic women have been much more afraid of falling ill, and the pandemic itself causes more trauma and stress for them than for men.
Studying the determinants of fear of COVID-19 is important for instance for disease prevention, as fear influences the extent to which people maintain social distancing, adhere to hand washing guidelines, and get vaccinated to protect themselves against COVID-19 infection. Furthermore, due to the novel nature of COVID-19 and the psychological stress associated with it, assessing fear of COVID-19 and studying its predictors makes it possible to develop appropriate prevention and support programs and to address them to specific groups of people (Pakpour & Griffiths, 2020).
On the one hand, fear of COVID-19 can have a paralyzing effect and thus foster the development of mental illness, significantly reducing perceived quality of life. This concerns situations when its level is high. On the other hand, however, it can mobilize one to adhere to recommendations such as social distancing, wearing protective masks, or disinfecting hands and touch surfaces. Last but not least, fear of COVID-19 may also contribute to the decision to get vaccinated against the disease.
In Poland, the public attitude towards adherence to COVID-19 recommendations changed each month as the pandemic continued. In spring 2020, the vast majority of the Polish population reduced social contacts, kept their distance, wore protective masks and disinfected their hands and touch surfaces. As time passed, these behaviors became less and less frequent. One of the reasons for this might have been the fact that people were becoming accustomed to living in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic, and consequently had a low level of fear of the disease, presented in particular by young people.
The scale of non-compliance with the legal provisions on the part of the general public is the result of historical circumstances on the one hand, and of the institutional environment on the other hand. Despite the changes it has undergone in the recent decades, the Polish society still differs from the open society of the Western type. In the Polish case, one can speak of a shortage of cultural resources, an essential category of which is social trust, including trust in authority. Society in Poland is characterized by a culture of distrust found at all levels of social life (Sztompka, 1996). The origins of this syndrome should be sought not only in the legacy of real socialism, but also in the experiences of the transformation period and in the related crises. The high degree of vaccine skepticism and one of the highest mortality rates in Europe represent a visible result reflecting not the decades of living under communism, but the decades of social consequences of its collapse. Low trust in the political elite translates, therefore, into selective compliance with the government’s recommendations. These trends were additionally reinforced by the increasing information chaos and restrictions introduced without justification (e.g., the ban on entry to forests).
The Polish society, as a result of diverse historical experiences, differs significantly from the societies of Western European or North American countries, but also from Asian ones. Citizens in Western Europe, North America, as well as in highly developed Asian countries generally comply with the regulations and recommendations of the authorities, including pandemic recommendations. This happens even in a place such as China, with the pandemic restrictions more stringent than in Poland. The Polish distrust of authority may have contributed not only to non-compliance with pandemic restrictions, but also to the low level of fear which we diagnosed among university students in Poland.
Limitations
The present study has several limitations. Firstly, an online survey addressed to random respondents being university students weakens the generalizability of its results. The data was collected from the respondents on a voluntary basis on the basis of an online application, which advises caution when making certain generalizations. Another limitation is the fact that although the study was conducted on a relatively large sample, it used a cross-sectional method of data collection. More reliable results could be obtained using a longitudinal study design. Further research is most definitely needed to identify further significant factors influencing student behavior during the pandemic.
Conclusions
The present study focused on whether the experience of COVID-19 disease (whether direct or among loved ones) was linked to fear among university students in Poland. According to the results, students generally presented a relatively low level of fear. Having suffered from the disease and knowing someone who had had light or asymptomatic COVID was not associated with higher levels of fear. This was only implied when the respondent knew someone who had been severely ill with or died of COVID-19. The level of fear was differentiated by gender (it was higher in the female group).
The study discussed here fits within the line of research on fear during the COVID-19 pandemic. One of the determinants of this fear, namely the experience of COVID-19 disease, is discussed here. Low fear has been found among students in the study. It thus provides data important for both theory and practice.
Supplemental Information
Additional Information and Declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Author Contributions
Elżbieta Turska conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, prepared figures and/or tables, and approved the final draft.
Natalia Stępień-Lampa conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, authored or reviewed drafts of the article, and approved the final draft.
Paweł Grzywna conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, authored or reviewed drafts of the article, and approved the final draft.
Human Ethics
The following information was supplied relating to ethical approvals (i.e., approving body and any reference numbers):
The Research Ethics Committee of the University of Silesia in Katowice granted Ethical approval to carry out the study within its facilities (KEUS.95/02.2021).
Data Availability
The following information was supplied regarding data availability:
The data is available at OSF: Stępień-Lampa, N., Turska, E., & Grzywna, P. Ł. (2022, April 26). Fear of COVID-19. Retrieved from osf.io/s47hx.
Grzywna Paweł, & Turska Elżbieta. (2022). Experience of COVID-19 disease and fear of the SARS-CoV-2 virus among Polish students (Version 1) [Data set]. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7295270.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Excellence Initiative of the University of Silesia in Katowice. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.