PeerJ Section
Bioinformatics and Genomics
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 7.3 (view impact metrics).
62,290 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Bioinformatics and Genomics articles 
3 April 2025
A multi-center cross-sectional investigation of BRAF V600E mutation in Ameloblastoma
"The article includes a large sample size in an understudied population, thus contributing to the literature exploring the effect of BRAF mutations in ameloblastoma"
 Renan de Souza, Handling Editor
Renan de Souza, Handling Editor
 Renan de Souza, Handling Editor
Renan de Souza, Handling Editor
2 April 2025
Seasonal genetic variation and genetic structure of Spodoptera exigua in Liaoning Province, Northeast China: insights from 11 years of microsatellite data
"This study provides meaningful insights into the seasonal genetic variation and population structure of Spodoptera exigua in northern China, addressing a notable research gap in understanding this agricultural pest's population dynamics. The research employs microsatellite analysis over a substantial time period (2012-2018), which strengthens the reliability of its findings. The identification of two distinct genetic groups and the observation of seasonal genetic subconstruction patterns contribute to our understanding of BAW migration patterns. These findings have practical implications for pest management, as understanding genetic variation and population structure can inform the development of control strategies. The methodology used is appropriate for the research objectives, and the results are presented with suitable analytical depth. While the study is geographically limited to Northeast China, its approach and findings may be applicable to BAW research in other regions. The research demonstrates a clear connection between basic population genetics research and its practical applications in agricultural pest management, making it a useful addition to the existing literature on migratory pest populations."
 Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
19 March 2025
A comprehensive prognostic and immunological analysis of hexokinase domain containing protein-1 (HKDC1) in pan-cancer
"This paper demonstrates that the expression level of hexokinase domain-containing protein 1 (HKDC1) is involved in cancer prognosis, providing important insights into HKDC1-targeted cancer therapy."
 Tokuko Haraguchi, Handling Editor
Tokuko Haraguchi, Handling Editor
 Tokuko Haraguchi, Handling Editor
Tokuko Haraguchi, Handling Editor
11 March 2025
Mining of co-expression genes in response to cold stress at maize (Zea mays L.) germination and sprouting stages by weighted gene co-expression networks analysis
"This study addresses a agricultural challenge by investigating low-temperature stress response in maize during critical growth stages. The research combines transcriptome sequencing with weighted gene co-expression network analysis to understand gene expression patterns between temperature-tolerant and sensitive maize lines. The methodology is systematic, employing multiple analysis approaches including WGCNA, GO, and KEGG pathway analysis. The identification of specific gene modules and pathways associated with low-temperature tolerance provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of cold stress response. The study's findings, particularly the validation of seven genes involved in low-temperature stress response, contribute to the existing knowledge base in crop stress biology. While the research is focused on maize, the methodological framework and findings may be applicable to understanding cold tolerance in other crops. The study has practical implications for crop improvement programs, especially in regions where early spring low temperatures affect maize production. However, additional research would be needed to validate these findings in field conditions and to determine the practical applications in breeding programs. The study represents a step forward in understanding cold tolerance mechanisms, though further work is required to fully utilize these insights in agricultural applications."
 Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
Fanglin Guan, Section Editor
24 February 2025
Injecting structure-aware insights for the learning of RNA sequence representations to identify m6A modification sites
"The authors introduced M6A-SAI, showcasing its effectiveness as a reliable method for identifying RNA m6A modification sites. The current revised version provides a clear and detailed explanation of the proposed identification methods, emphasizing their robustness. M6A-SAI proves to be highly beneficial in advancing RNA biology."
 Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
 Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
13 February 2025
Integrated genomic analysis of the stemness index signature of mRNA expression predicts lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and immune landscape
"This study addresses a gap in understanding the prognostic value of mRNAsi in LUAD by establishing a novel risk model based on eight mRNAsi-related genes. The research demonstrates that low mRNAsi levels correlate with improved prognosis in LUAD patients, and the developed risk model shows potential in predicting patient outcomes. The identification of differential gene expression patterns between risk groups, particularly in metabolic and cell cycle pathways, provides insights into underlying mechanisms. The study's findings regarding the relationship between risk scores and immune cell infiltration, along with TIDE scores, suggest implications for immunotherapy response prediction. The validation of the eight-gene signature through RT-qPCR and functional studies of EIF5A adds experimental support to the bioinformatic findings. By integrating multiple analytical approaches, including drug sensitivity assessment, this work presents a practical tool for clinical prognosis evaluation and treatment strategy selection in LUAD. While further validation in larger cohorts would be beneficial, this study contributes to the growing body of knowledge on personalized treatment approaches in lung adenocarcinoma and may assist clinicians in making more informed decisions regarding patient care."
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
12 February 2025
PGSXplorer: an integrated nextflow pipeline for comprehensive quality control and polygenic score model development
"This manuscript presents a user-friendly pipeline for polygenic score model development, with implications for genomic research and personalized medicine."
 Burcu Bakir-Gungor, Handling Editor
Burcu Bakir-Gungor, Handling Editor
 Burcu Bakir-Gungor, Handling Editor
Burcu Bakir-Gungor, Handling Editor
10 February 2025
A gene signature related to programmed cell death to predict immunotherapy response and prognosis in colon adenocarcinoma
"This study provides a systematic analysis of programmed cell death-related genes in colon adenocarcinoma, addressing a certain gap in understanding the relationship between PCD genes and COAD progression. The research employs multiple computational approaches and experimental validation to develop a risk prediction model based on six PCD-related genes. The study's methodology is comprehensive, integrating consensus clustering, immune infiltration analysis, and pathway enrichment analysis, supported by functional experiments. The identification of two distinct subtypes (S1 and S2) and the establishment of a six-gene Riskscore model contribute to the current knowledge of COAD prognosis assessment. The research reveals meaningful associations between risk scores and immune checkpoint expression, TIDE scores, and somatic mutations, particularly in TP53. While the findings require further validation in larger cohorts, this work presents a reasonable framework for prognostic evaluation in COAD patients and may inform treatment strategy selection. The integration of multiple prognostic factors into a nomogram demonstrates practical clinical potential, though additional prospective studies would be beneficial to confirm its utility. This research adds to the growing body of knowledge regarding molecular stratification in COAD and may support clinical decision-making."
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
20 January 2025
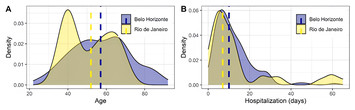
Genetic determinants of COVID-19 severity and mortality: ACE1 Alu 287 bp polymorphism and ACE1, ACE2, TMPRSS2 expression in hospitalized patients
"Understanding of the genetic basis of COVID-19 is still very important, and this manuscript presents an important contribution to this goal."
 Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
 Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
23 December 2024
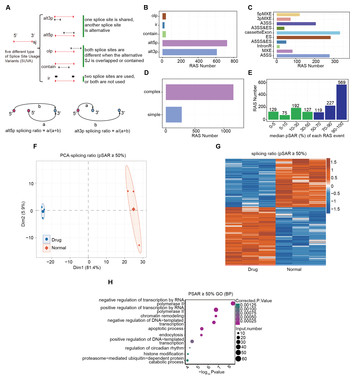
Identification of the whole genome of alternative splicing and RNA-binding proteins involved in nintedanib-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
"Authors focused on alternative splicing and RNA binding proteins impact in apoptosis process and key influence in the gastric cancer. This concept more useful in the area of gastric cancer research."
 Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
 Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
Praveen Korla, Handling Editor
Collections
View all 
PeerJ Expert Curations: Molecular Ecology
RiTA 2023: Robotics and AI for Digital Futures

International Conference on Machine Learning and Intelligent Systems (MLIS)

Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Role of AI and Machine Learning

Artificial Intelligence for Mental Health: Advancements, Challenges, and Ethical Implications

62,290 Followers


