Genome-wide identification, expression pattern and interacting protein analysis of INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) gene family in Phalaenopsis equestris
- Published
- Accepted
- Received
- Academic Editor
- Lin Zhang
- Subject Areas
- Agricultural Science, Bioinformatics, Molecular Biology, Plant Science
- Keywords
- IDD gene family, Expression profile, Phylogenetic analysis, Protein interaction, Phalaenopsis equestris, Promoter analysis, Stress response, Hormone response, Transcription factor, Chromatin remodeling factors
- Copyright
- © 2024 Zhang et al.
- Licence
- This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed. For attribution, the original author(s), title, publication source (PeerJ) and either DOI or URL of the article must be cited.
- Cite this article
- 2024. Genome-wide identification, expression pattern and interacting protein analysis of INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) gene family in Phalaenopsis equestris. PeerJ 12:e18073 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.18073
Abstract
The plant-specific INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) gene family is important for plant growth and development. However, a comprehensive analysis of the IDD family in orchids is limited. Based on the genome data of Phalaenopsis equestris, the IDD gene family was identified and analyzed by bioinformatics methods in this study. Ten putative P. equestris IDD genes (PeIDDs) were characterized and phylogenetically classified into two groups according to their full amino acid sequences. Protein motifs analysis revealed that overall structures of PeIDDs in the same group were relatively conserved. Its promoter regions harbored a large number of responsive elements, including light responsive, abiotic stress responsive elements, and plant hormone cis-acting elements. The transcript level of PeIDD genes under cold and drought conditions, and by exogenous auxin (NAA) and abscisic acid (ABA) treatments further confirmed that most PeIDDs responded to various conditions and might play essential roles under abiotic stresses and hormone responses. In addition, distinct expression profiles in different tissues/organs suggested that PeIDDs might be involved in various development processes. Furthermore, the prediction of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) revealed some PeIDDs (PeIDD3 or PeIDD5) might function via cooperating with chromatin remodeling factors. The results of this study provided a reference for further understanding the function of PeIDDs.
Introduction
Spatio-temporal specific expression of genes is the basis of cell differentiation in multicellular organisms, in which transcription factors (TFs) play dominant roles in controlling gene expression by recognizing and binding special cis-elements. The INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) genes encode a plant-specific family of zinc finger TFs, which is characterized by a conserved ID domain that consists of two C2H2 and two C2HC fingers (Colasanti et al., 2006). IDD genes have been identified in many plants and are widely reported to involve in plant growth and development, and adaptation to environment.
The identification and function analysis of IDD genes originated from crop and model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Sixteen, fifteen, and twenty-two IDD genes have been identified in Arabidopsis, rice, and maize, respectively (Coelho et al., 2018; Feng et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020). These IDD genes are involved in different developmental processes and stress response. In root development, AtIDD3/MAGPIE (MAG) and AtIDD10/JACKDAW (JKD) were reported to regulate tissue boundary formation by cooperating with SHR (SHORT-ROOT) and SCR (SCARECROW) (Long et al., 2015; Ogasawara et al., 2011). OsIDD10 was involved in the seminal root development of rice seedling via mediating N-linked metabolic responses (Xuan et al., 2013). During seed formation process, AtIDD1/ENHYDROUS (ENY) regulated light and hormonal signal pathway and eventually promoted seed germination (Feurtado et al., 2011). Duplicated IDD genes (ZmIDDveg9 and ZmIDD9) encoded NKD (naked endosperm) proteins that were required for maize aleurone cell fate and cell differentiation (Yi et al., 2015; Gontarek et al., 2016). To the leaf and shoot development, AtIDD4/IMPERIAL EAGLE and other four AtIDD s (AtIDD5, AtIDD10, AtIDD11, and AtIDD14), as downstream genes of REV (REVOLUTA), involved in the ad/abaxial regulatory network (Reinhart et al., 2013). OsIDD14/Loose Plant Architecture1 (LPA1), the ortholog gene of AtIDD15, had distinct functions from AtIDD15 (Cui et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2016). As a part of the complicated regulatory network, OsIDD14 affected the sedimentation rate of amyloplasts and shoot gravitropism of rice (Wu et al., 2013). GA homeostasis and sugar metabolism are associated with flowering. AtIDD8 promoted flowering by activating the expression of two sucrose synthesis genes (SUS1 and SUS4) (Seo et al., 2011b). AtIDD2 (GAI-ASSOCIATED FACTOR1, GAF1) encodes a DELLA-Interacting protein. Overexpression of GAF1 resulted in flowering earlier, while gaf1 flowered slightly later than WT (wild type) under short-day conditions. The GA-related phenotype of gaf1 suggested GA responsiveness was affected (Fukazawa et al., 2014). The variations in sucrose and starch levels revealed the cause of an extreme late-flowering phenotype of zmid1 (Coneva et al., 2012). In addition, OsID1, a rice ortholog gene of ZmID1, acted as a flowering promoter by regulating flowering-related gene expression (Matsubara et al., 2008). For stress response, AtIDD14 generated two splice variants (AtIDD14α and AtIDD14β). The functional AtIDD14α had DNA binding activity and could promote starch degradation. AtIDD14β form was cold-induced produced and bound with AtIDD14α to repress AtIDD14α function so as to help plants to tolerate low temperature (Seo et al., 2011a). Recent research suggested AtIDD14 also regulated drought tolerance by interacting with bZIP-type ABFs/AREBs (Liu et al., 2022). AtIDD4 was identified as a negative regulator of salt stress, and overexpression of AtIDD4 resulted in hypersensitive to salt-stress (Rawat et al., 2023). ROC1 (regulator of CBF1), an IDD protein of rice, was verified as a chilling tolerance regulator based on the cold sensitive phenotype and lower level of CBF1 transcripts in roc1 mutant (Dou et al., 2016). OsIDD12, OsIDD13, and OsIDD14 could form a transcription complex to activate the expression of MDPK (Malectin Domain Protein Kinase) to enhance resistance of ShB (Sheath blight) (Cui et al., 2022).
With the deepening of the research, IDD genes gained more and more attention and had been explored in ornamental plants. In a comparative genomic analysis of the IDD gene family in five Rosaceae species, 16 IDD genes were determined in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and most of PbIDD s have a high transcription level in productive organs (Su et al., 2019). The comprehensive analysis of IDD genes in apple identified 20 putative IDD genes and these IDD genes responsed to various circumstances (Fan et al., 2017). Peach (Prunus persica) has 14 IDD genes, and PpIDD4, PpIDD12, and PpIDD13 can interact with DELLA1, a vital factor in GA signaling pathway, to participate in GA feedback regulation (Jiang et al., 2022).
Phalaenopsis equestris, known for its butterfly-shaped flowers and brilliant colors, is a widely cultivated flowers and of great economic importance. Despite extensive studies of IDD genes were under way, little is known about the features of PeIDD s. Due to the genome sequence of P. equestris has emerged recently (Cai et al., 2015), the opportunity arises to conduct the comprehensive study of the PeIDD family. In this study, 10 PeIDD s were identified from P. equestris. Phylogenetic relationship, gene structure, protein structure and gene expression profile of 10 PeIDD s were carried out. More importantly, we predicted the interaction proteins of PeIDDs. The results will provide a certain theoretical basis for further research on th functions of PeIDDs.
Materials and Methods
Identification of IDDs in P. equestris and phylogenetic analysis
The P.equestris genome sequence and annotation file were download from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=txid78828[orgn]&shouldredirect=false). AtIDD and OsIDD proteins were downloaded from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) database (https://www.arabidopsis.org) and The Rice Genome Annotation Project Database and Resource (http://rice.uga.edu/index.shtml) (Table S1), respectively. To identifiy potential IDDs in P. equestris, 16 AtIDD and 15 OsIDD proteins were used as query sequences in a BLAST search with default parameters in TBtools v1.120 software (Chen et al., 2020). In addition, all candidate PeIDD proteins were verified according to the method of previous report (Jiang et al., 2022) to confirm IDD domains. Incomplete and redundant protein sequences were discarded manually. Subsequently, physicochemical properties (PIs, MWs) were predicted through the ExPASy website (https://www.expasy.org/).
Multiple sequence alignment of IDD proteins from Oryza sativa, A. thaliana and P. equestris was done using ClustalX 2.0 software (Larkin et al., 2007). The sequence alignment results were used to construct the neighbor-joining (NJ) tree by MEGA 7.0 software (Kumar, Stecher & Tamura, 2016), with the following parameters: Poisson correction, complete deletion, and bootstrap (1,000 replicates).
Gene structures analysis, conserved motifs prediction, and cis-element analysis of the promoters
The gene structures of PeIDDs were determined by DNA and cDNA sequence alignment. The potentially conserved motifs of PeIDD proteins, including ID domain, were determined by the online Multiple Expectation for Motif Elicitation (MEME, http://meme-suite.org), (Bailey et al., 2009), using the following parameter settings: the maximum number of motifs, 10; the minimum width of motifs, 5; the maximum width of motifs, 20; and other default parameters. The promoter sequences of PeIDDs were harvested from NCBI website and its cis-acting elements were predicted using the PlantCARE database (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) (Lescot et al., 2002). All gene structures, conserved motifs, and cis-elements were visualized by running the IBS version 1.0.2 software (Liu et al., 2015).
Protein interaction prediction
The online STRING platform (https://string-db.org) (Szklarczyk et al., 2017) was used to predict the protein-protein network between PeIDDs and other proteins, using Dendrobium catenatum as reference organism, with the parameter: predicted interacting protein score above 0.4.
Plant materials, RNA extraction and qRT-PCR
Fifteen P. equestris was collected from Lufa Orchid (Taiwan, China) and placed in the greenhouse of Jingchu University of Technology. Roots, leaves, flowers, and floral stalks were sampled and immediately stored at −80 °C. For plant hormone and stress treatment, the plants were exposed to 0.2 M ABA, 10−6M NAA, 20% PEG6000, and 4 °C. Total RNA from different tissues was isolated by TransZol (ET101-01-V2; TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) reagent, and detected by NANODROP 1,000 spectrophotometer to determine the extraction quality, then reversed transcribed into cDNA with HiScript II Q RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper) (R223-01; Vazyme, Hangzhou, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA was diluted to 100 ng/µL and used as a template for RT-qPCR. Specific primers for 10 PeIDD genes with amplified size ranging from 170 to 250 bp were designed using online programs (https://sg.idtdna.com/scitools/Applications/RealTimePCR/) (Table S2). The RT-qPCR was performed on the QuantStudio 6 Flexreal-time PCR instrument (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). PeActin was used as an internal reference (F: GCTGAGGGAGGCAAGGATAGAT; R: GCACCCAGCAGCATGAAGATC) to standardize gene expression levels, and each cDNA was subjected to three biological replicates. The PCR mixture (10 µL) included 5 µL Taq Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Q712-02; Vazyme, Hangzhou, China), 10 mM of each primer, 100 ng cDNA template, and nuclease-free water. The PCR program was performed as follows: 95 °C for 10s; 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 40 s. Relative expression values were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method (Livak & Schmittgen, 2001) and visualized by GraphPad Prism 8.0.2.
Results
Genome-wide identification and characterization of PeIDD gene family
Using 16 AtIDD and 15 OsIDD protein sequences as the queries, 12 PeIDD proteins were initially identified by BLAST searches. Examined by ID domains, ten proteins were finally confirmed as PeIDD family members. According to the order distribution on the scaffolds (Fig. S1), these genes werer named PeIDD1-PeIDD10. The analysis of these PeIDD protein sequences (Table S3) revealed that the physicochemical properties of each member were different (Table S4). The amino acid lengths of the PeIDDs ranged from 197 aa (PeIDD3) to 480 aa (PeIDD1). The molecular weight (MW) ranged from 22,098.33 Da (PeIDD3) to 50,799.25 Da (PeIDD1). The isoelectric point (pI) of PeIDDs ranged from 8.71 (PeIDD10) to 9.56 (PeIDD3). The instability index spanned from 37.79 (PeIDD8) to 89.71 (PeIDD3).
Phylogenetic analysis of PeIDDs
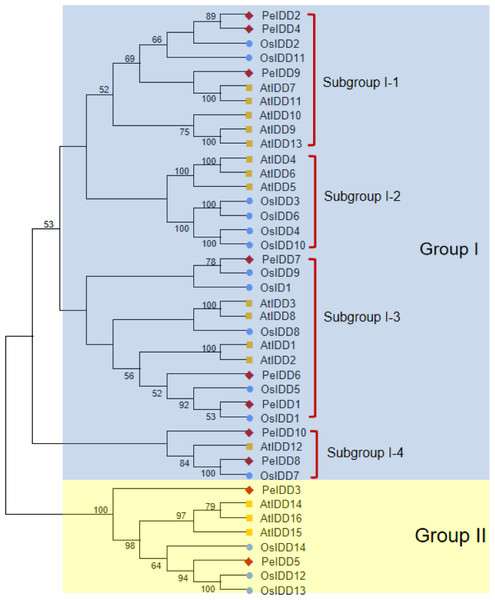
To better understand the phylogenetic relationship of IDDs in A. thaliana (16 members), O. sativa (15 members) and P. equestris (10 members), a neighbor-joining (NJ) tree of 41 IDD proteins was constructed based on their full length amino acid sequences. All IDD proteins were clearly divided into two groups (I and II) (Fig. 1). Group I had a large number of member, with 13 AtIDDs, 12 OsIDDs, and 8 PeIDDs, accounting for 80.5% of the total IDD proteins. While group II only harbored 8 IDD proteins (three AtIDDs, three OsIDDs, and two PeIDDs). On the basis of the bootstrap values and topological structure, group I can be divided into four subgroups. Interesting, subgroup I-2 were solely composed of AtIDDs and OsIDDs. In other subgroups of group I (subgroup I-1, I-3, and I-4), most PeIDDs were clustered with OsIDDs firstly, suggesting that PeIDDs might have a close relationship to OsIDDs.
Figure 1: Phylogeny of IDD homologs in Phalaenopsis equestris (Pe,red diamond), Oryza sativa (Os, blue circles), and Arabidopsis thaliana (At, yellow squares).
Cluster X and MEGA 7.0 were used to align the protein sequences and generate the neighbor-joining (NJ) tree, respectively. Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) more than 50% were shown on branches.Gene structure and motif composition of PeIDD gene family
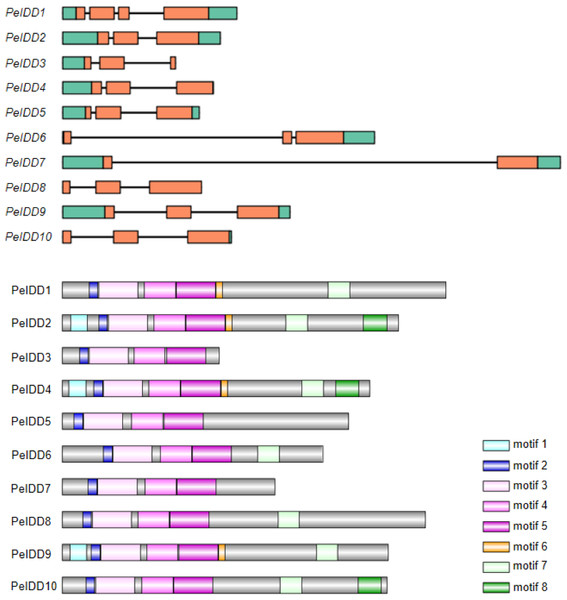
To gain more insight into the potential relationship about gene structure-function and protein structure-function, gene structure and motif prediction of PeIDDs were determined. For the exon-intron structures, most PeIDDs displayed three exons, whereas PeIDD1 and PeIDD7 had four and two exons, respectively (Fig. 2A). The length of exons was similar, while the intron lengths varied greatly (Fig. 2A). In particular, PeIDD6 and PeIDD7 had exceptionally long introns, which was similar to the KNOX gene structure of orchids and might be unique to Orchidaceae (Zhang et al., 2022). In P.equestris genome, half of PeIDDs (PeIDD3, PeIDD4, PeIDD6, PeIDD8 and PeIDD10) had no 5′-UTR, 3′-UTR, and both UTRs (5′-UTR and 3′-UTR) (Fig. 2A). This suggested that they were likely the UTR-less IDD genes in P. equestris.
Figure 2: Gene structures and conserved motifs in PeIDDs.
(A) Gene structures were visualized using IBS1.0.2. UTRs and exons were represented by green and red boxes, respectively. (B) Conserved motifs were identified using the online MEME program and represented by different colored boxes. Motif sequences were shown in Fig. S2.Subsequently, MEME (http://meme-suite.org) was used to predict the putative motifs shared among PeIDD proteins. In total, 8 types of motifs were observed (Fig. 2B, Fig. S2). Motif 2, 3, 4, and 5 were widespread at the N-terminus of all PeIDDs. Motif 2 encoded a nuclear localization signal (NLS), indicating that all PeIDDs are located in the nucleus. Motif 3, 4, and 5 constituted the conserved ID domain, which was the unique structure of IDDs. Motif 1 was specific to the PeIDDs (PeIDD2, PeIDD4, and PeIDD9) of subgroup I-1 (Fig. 1). Motif 6, following the ID domain, only existed in PeIDD1, PeIDD2, PeIDD4, and PeIDD9. Motif 7 (“MSATALLQKAA” domain) and motif 8 (“TRDFLG” domain) that were verified to act in protein-protein interactions (Colasanti et al., 2006) were found in the C terminus of most PeIDDs. Because motifs are associated with protein interactions or binding to target genes, differences in motif composition suggest that these PeIDDs may function in different mechanisms.
Cis-regulatory elements analysis of PeIDD genes
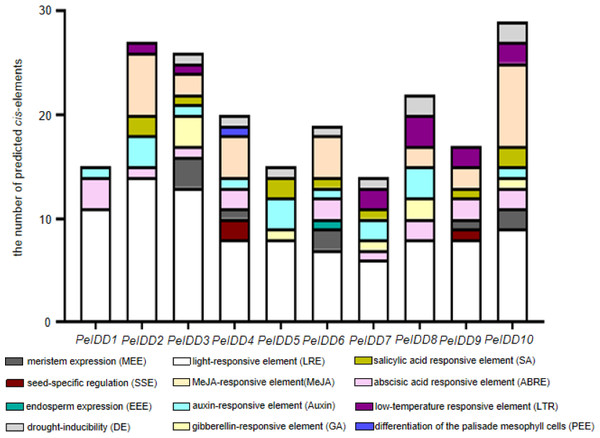
In order to a space between the two words in the promoter regions of PeIDDs, 2,000 bp sequences upstream of transcription start site of PeIDDs were retrieved as the promoters (Table S5), and then submitted them to the PlantCARE database. A large number of cis-elements were obtained and could be classified into three types: growth and development-related, phytohormone responsive, and abiotic stress responsive (Table S6). Growth and development-related elements consisted of LRE (light responsive element), SSE (seed-specific regulation element), MEE (meristem expression element), PEE (palisade mesophyll cells expression element), and EEE (endosperm expression element). Hormone responsive elements included ABA, GA, Auxin, SA, and MeJA. Abiotic stresses responsive elements were low-temperature responsive element and drought-related element (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: The types and numbers of predicted cis-elements in the promoter of the PeIDD genes.
Details information of predicted cis-elements in PeIDD genes were listed in Table S6 . Various cis-elements were shown by different colored boxes.Among these growth and development-related cis-elements, LREs were the most frequently occurring responsive elements, suggesting that PeIDDs might play important roles in P. equestris light morphogenesis. Plant hormones are also essential to plant growth and development. ABA-responsive elements (ABRE) and Auxin-responsive elements (TGA-element, AuxRR-core) were observed in nine PeIDDs. SA responsive elements (TCA-element) and MeJA responsive elements (TGACG-motif, CGTCA-motif) existed in seven PeIDDs. GA responsive elements (P-box, TATC-box, GRAE-motif) were found in five PeIDDs. The widespread distribution of hormone response elements in the promoter indicated that PeIDDs might be widely involved in hormone signal pathway.
The adaptability to the environment is a focus in plant breeding. Two cis-elements related to abiotic stress, namely, drought response element (LTR) and low temperature response element (DE), appeared in the promoter of PeIDDs. DE existed in seven PeIDDs, and LTR was present in six PeIDDs. These results suggested that PeIDDs might play a vital role in stress adaptation.
Expression patterns of PeIDD genes in different tissues
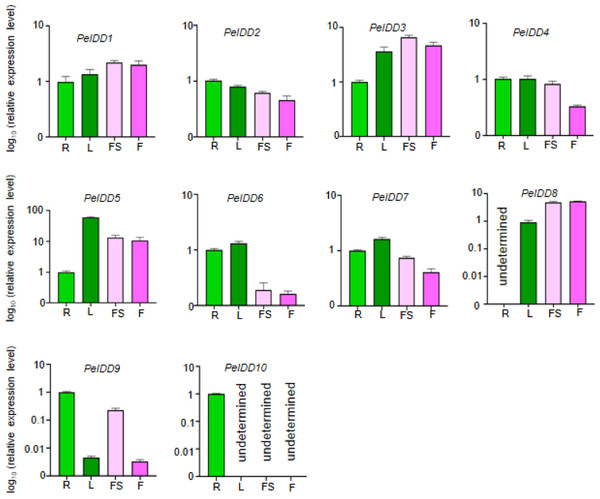
The tissue-specific expression patterns of the PeIDD gene family were investigated in four tissues/organs, including root, flower, leaf, and floral stalk. The results revealed that the PeIDDs exhibited different expression level in these tissues. Seven PeIDDs (PeIDD2, PeIDD4, PeIDD5, PeIDD6, PeIDD7, PeIDD9, and PeIDD10) showed high transcripts in vegetative tissues (root and leaf), but relatively low expression levels in the reproductive tissue (flower and floral stalk) (Fig. 4). Among them, PeIDD5 was predominantly expressed in leaf (Fig. 4), hinting PeIDD5 might participate in leaf development. PeIDD9 and PeIDD10 were highly expressed in the root, especially PeIDD10 was expressed specifically in the root and barely detected in other tissues (Fig. 4), indicating PeIDD9 and PeIDD10 might regulate root development. The transcript levels of PeIDD1, PeIDD3, and PeIDD8 displayed higher expression in floral stalk and flower (Fig. 4), suggesting they might be involved in flower development.
Figure 4: The expression profiles of PeIDD genes in roots (R), leaves (L), floral stalks (FS), and flowers (F).
Three independent experiments were performed and the means were represented by error bars. PeIDDs transcript levels were normalized to PeActin.Response of PeIDD genes to plant hormones and abiotic stress
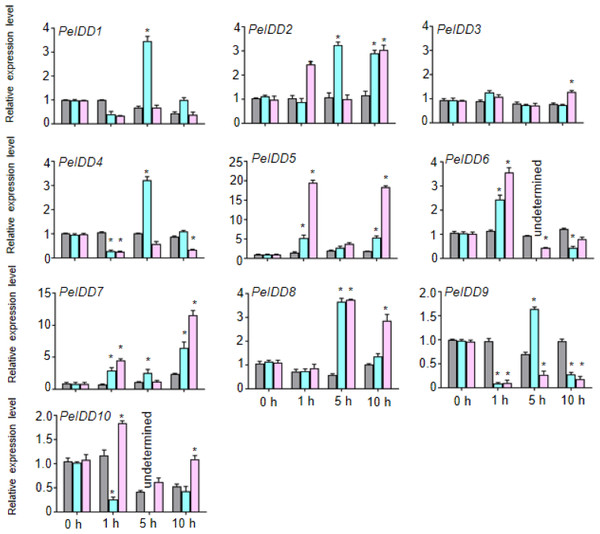
Because of lots of hormone and stress responsive elements were found in the promoter of PeIDDs, the expression patterns of PeIDDs under hormones (ABA and NAA) and stresses (drought and cold) during the different time courses (0 h, 1 h, 5 h, and 10 h) were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Under 0.2 M ABA treatment, seven PeIDDs (except PeIDD3, PeIDD7, and PeIDD10) expression levels reached their peaks after 1 h or 5 h. PeIDD7 was induced at 1 h and peaked after 10 h, while PeIDD3 showed no significant changes and the expression of PeIDD10 was inhibited (Fig. 5). After NAA treatment 1 h, PeIDD1, PeIDD4 and PeIDD9 transcripts had a significant decline compared with the untreated group, while the expression levels of PeIDD2, PeIDD5, PeIDD6, and PeIDD7 showed an over two-fold increase. PeIDD8 was obviously upregulated after NAA treatment 5 h (Fig. 5).
Figure 5: The expression patterns of PeIDDs under ABA and NAA treatment.
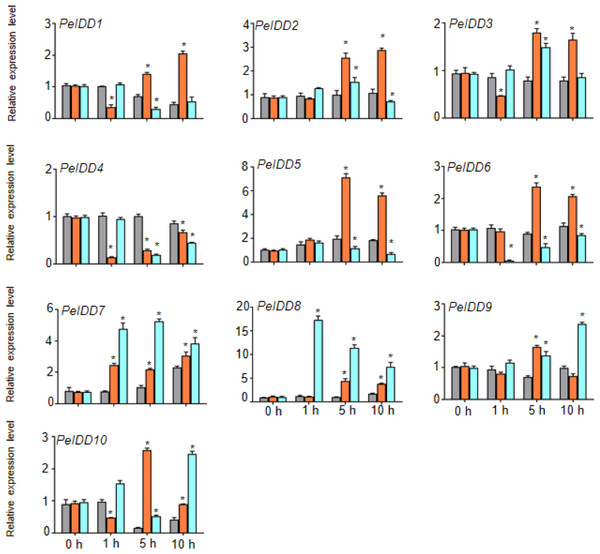
PeIDD transcript levels were determined by RT-qPCR under different plant hormone. Grey, blue and pink bars represented untreated, ABA treated, and NAA treated groups, respectively. The PCR signals were normalized with those of PeActin transcripts. The SDs (standard deviations) of the means of three independent biological replicates were denoted by error bars. Statistically significant differences between untreated and treatment groups were analyzed by an independent Student’s t-tests and shown by asterisks (∗ P < 0.05).Regardless of whether PeIDDs had drought responsive elements or not (Fig. 3, Table S4), all PeIDDs responded to drought at different time points. Nine PeIDDs showed at least two-fold increase of transcripts, while PeIDD4 exhibited down-regulation of transcript level. The results revealed that PeIDDs might be widely involved in drought response. Under cold treatment, these results were related to the number of LTRs in the promoter of PeIDDs (Fig. 3, Table S4). For example, four PeIDDs (PeIDD7, PeIDD8, PeIDD9, and PeIDD10) contained two or three LTRs and showed obvious induced expression (Fig. 6), among which the expression of PeIDD 8 increased more than 8-fold after 1 h of treatment. PeIDD2 and PeIDD3 had one LTR and exhibited a slight increase in expression. However, PeIDD1, PeIDD4, PeIDD5, and PeIDD6 had no LTR elements, their expression level was down-regulated after cold stress (Fig. 6), which suggested that they might be regulated indirectly or had other unknown cold responsive elements.
Figure 6: The expression patterns PeIDDs under drought and cold stress.
PeIDD transcript levels were determined by RT-qPCR under different abiotic stresses. Grey, red and blue bars represented untreated, drougt, and cold stress groups, respectively. The PCR signals were normalized with those of PeActin transcripts. The SDs (standard deviations) of the means of three independent biological replicates were denoted by error bars. Statistically significant differences between untreated and treatment groups were analyzed by an independent Student’s t-tests and shown by asterisks (∗P < 0.05).Prediction of protein interaction network of PeIDD proteins
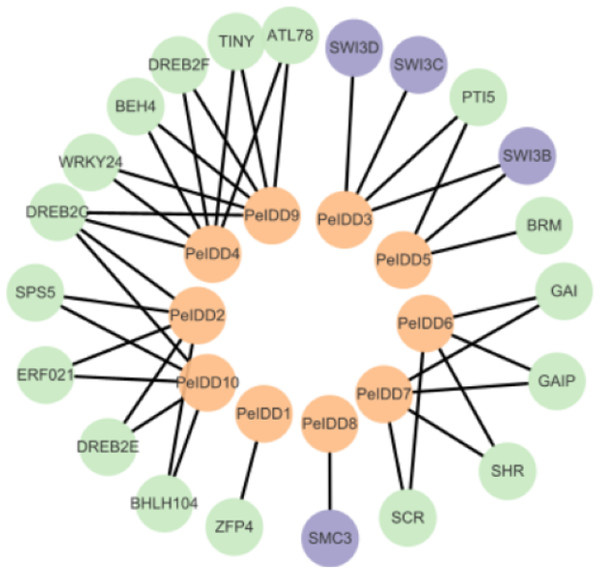
Although the function of PeIDDs has not been reported, understanding the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network may help us understand their regulatory mechanism. Based on the prediction results from the STRING website (Table S5), the interaction network was constructed by Cytoscape software. The results showed PeIDDs could interact with 21 proteins, including TFs (5), chromatin remodeling factors (4), enzymes (2), and other proteins (10) (Fig. 7, Table S5). Among TFs, ERF021 and TINY are ethylene responsive factors (Xie et al., 2019). PeIDD2 and PeIDD10 could interact with ERF021 and PeIDD4 with TINY, suggesting that the three PeIDDs might be integrated into the ethylene response pathway. WRKY family is known to involve in biotic and abiotic stress response (Wani et al., 2021; Khoso et al., 2022). WRKY24 was predicted to interact with PeIDD4 and PeIDD9, indicating PeIDD4 and PeIDD9 might participate in stress adaptation. PTI5 is a pathogenesis-related transcriptional activator (Wang et al., 2021). PeIDD5 might be involved in plant immune response by interacting with PTI5. Among chromatin remodeling factors, SWI/SNF (SWITCH/SUCROSE NONFERMENTING) was reported to regulate chromatin structure (Bieluszewski et al., 2023). PeIDD3 and PeIDD5 were predicted to act with SWI3 subunit, indicating PeIDD3 and PeIDD5 might regulate transcript levels of their target genes by recruiting chromatin remodeling factors. The interaction of PeIDD8 to SMC3 (structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 3) indicated that PeIDD8 might help to stabilize chromosome structure. ATP-dependent helicase BRM is one of the enzymes that PeIDDs bound. Its interaction protein PeIDD5 might help it locate to specific chromatin regions. Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein (DREB) and the SHR-SCR (SHORTROOT-SCARECROW) complex stood out among the other proteins. PeIDD2, PeIDD4, PeIDD9, and PeIDD10 could interact with DREB, indicating that they could participate in drought responses. SHR-SCR complex was reported to involve in root development (Shaar-Moshe & Brady, 2023), suggesting that PeIDD6 and PeIDD7 might be in a common regulatory pathway with it. These results fully demonstrated the function diversity of PeIDDs and the complexity of the regulatory pathways.
Figure 7: Protein–protein interaction network of PeIDDs.
Orange, purple, and green circles represented PeIDDs, epigenetic factors (SWI3) and structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC3), and other proteins, respectively. The information of interacting proteins was shown in Table S7.Discussion
P. equestris is an ornamental plant and known for its elegant appearance and extended longevity. A comprehensive understanding of P. equestris IDD gene family, and making use of them, will help to enhance the growth and ornamental value of P. equestris. Here, a total of ten PeIDD genes were identified in the P. equestris genome, their expression profiles in different tissues, under hormone and stress treatment, and interaction proteins information were determined.
According to protein sequence similarity, all PeIDDs identified in this study were classified into two groups (group I and II) (Fig. 1), which was consistent with the classification of IDD proteins in rice (Zhang et al., 2020), Phyllostachys edulis (Guo et al., 2022), and Arabidopsis (Coelho et al., 2018). These IDD proteins in different groups/subgroups might have been functionally diverged and involved in different biological processes. In subgroup I-2, AtIDD4, AtIDD6 and OsIDD10 were related to root development (Moreno-Risueno et al., 2015; Yoshida et al., 2014; Xuan et al., 2013). In subgroup I-3, OsID1 and OsIDD1 are flowering regulator (Wu et al., 2008; Deng et al., 2017). Among PeIDD proteins in the same subgroup, PeIDD1 clustered with OsIDD1 firstly and PeIDD7 with OsID1 (Fig. 1). Combined higher expression level of PeIDD1 in flower (Fig. 4), we speculated that PeIDD1 might be involved in flowering of P. equestris. As flowering factors controlling the phase transition from vegetative to reproductive phase, OsID1 and OsIDD1 proteins differ in motif composition. OsIDD1 had motif 7 at the C-terminus, OsID1 did not (Zhang et al., 2020). This indicated that there might be differences in regulating rice flowering mechanism between OsID1 and OsIDD1. PeIDD1 also had motif 7 (Fig. 2), suggesting PeIDD1 might have similar mechanism of promoting flowering to OsIDD1. Taken together, PeIDD1 might be a potential target gene for regulating flower development in P. equestris, which needs further experiments to verify its function.
The cis-elements in the promoter determined the response of genes to environmental cues. The promoter of PeIDD genes contained a variety of cis-acting elements (Fig. 4, Table S4), which suggested that PeIDDs might function in various physiological processes and response to different signals. Hence, the expression level of all PeIDD genes to plant hormones and abiotic stresses were investigated by RT-qPCR (Figs. 5 and 6) and are mainly consistent with the cis-elements. Interesting, although not all PeIDD genes have drought-responsive elements, all PeIDDs responded to drought stress, whether their expression levels increased or decreased (Fig. 6). This indicated PeIDDs directly or indirectly involved in drought response, consistent with previous reports that IDDs might be related to the formation of Kranz ring in C4 plants and important in drought resistance (Coelho et al., 2018). Among PeIDD genes, PeIDD8 had the most cold-responsive elements (Table S4) and showed a rapid response to cold stress, with a sharp transcript level increase (Fig. 6). Low temperature seriously inhibits the growth of P. equestris. Based on the response of PeIDD8 to cold stress, PeIDD8 might act as an effective regulators to improve cold stress resistance/tolerance in P. equestris.
PPI prediction have been thought as an important content in gene family analysis, because it can help us to understand the molecular mechanism of protein function. In Brassica napus, Wang et al. (2018) predicted 38 proteins interacted with BnWOXs, including peptides, TFs, and other proteins. In rice, Zhang et al. (2020) predicted histone modifiers could interact with OsIDDs which indicated that OsIDDs might regulate the expression of downstream target genes through changing the chromatin structure. Interestingly, PPI analysis revealed that some PeIDDs (PeIDD3 and PeIDD5) could cooperate with chromatin remodeling factors (Fig. 7). Both chromatin remodeling factors and histone modifiers are epigenetic modifiers with the ability to alter chromatin structure. Consequently, interaction with epigenetic modifiers to regulate the expression of downstream genes might be a common regulation mode of IDDs.
Conclusions
In this study, ten PeIDDs were characterized and classified into two groups based on protein sequence and conserved motifs at the C-terminal. Expression profiles of PeIDDs under plant hormones and abiotic stresses suggested that PeIDDs might widely participate in hormone/abiotic stress signaling pathway. Importantly, PPIs analysis revealed some PeIDDs might interact with chromatin remodeling factors to modulate target genes expression. Taken together, our studies provided a theoretical basis for further analysis of the molecular mechanism of PeIDDs in P. equestris.
Supplemental Information
Locations of PeIDD genes
The blue bars indicate the different scaffolds of P. equestris genome.
Motif sequences of PeIDDs
Orange and blue triangles represented conserved C and H residues in the ID domains, respectively.