PeerJ Section
Bioinformatics and Genomics
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 6.1 (view impact metrics).
67,240 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Bioinformatics and Genomics articles

21 February 2024
DNA mini-barcoding reveals the mislabeling rate of canned cat food in Taiwan
"Information on accurate content in pet food is an important area of research, providing information to pet owners regarding the actual nutrition, but also as mentioned in the manuscript, other issues related to sustainability and species conservation."
 Brenda Oppert, Section Editor
Brenda Oppert, Section Editor
 Brenda Oppert, Section Editor
Brenda Oppert, Section Editor
14 February 2024
Fine-scale mapping of chromosome 9q22.33 identifies candidate causal variant in ovarian cancer
"The article advances our understanding of the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer."
 Philip Coates, Handling Editor
Philip Coates, Handling Editor
1 February 2024
In silico and in vitro evaluation of the anti-virulence potential of patuletin, a natural methoxy flavone, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
"This study suggest significance of Patuletin as a potential therapeutic agent in combination with antibiotics to combat antibiotic-tolerant P. aeruginosa infections. It will help to generate more effective antibiotics for antibiotic resistant microbes."
 Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
 Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
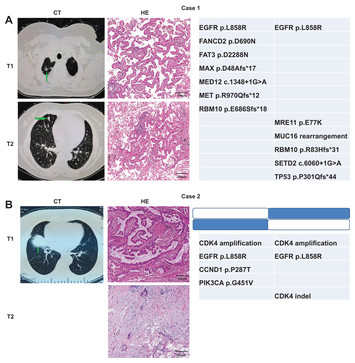
31 January 2024
Using molecular characteristics to distinguish multiple primary lung cancers and intrapulmonary metastases
"This article is important for several reasons and has significant implications for lung cancer research and clinical practice. The study addresses the challenge of distinguishing between multiple primary lung cancers (MPLC) and intrapulmonary metastasis (IPM), which can vary in clinical stage, treatment, and prognosis. Currently, the existing differentiation criteria based on histology alone are insufficient to meet the clinical needs, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive approach.
The significance of this study lies in the integration of histological analysis and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to develop detailed identification criteria for MPLC and IPM. By analyzing genomic profiles obtained from 450-gene-targeted NGS, the authors identified key differences in genetic mutations between MPLC and IPM. They found that MPLC cases had a low presence of trunk or shared mutations, while IPM cases exhibited a higher percentage of trunk and shared mutations. These findings provide novel insights into the genetic alterations associated with each condition and suggest that the type and number of shared variants, in addition to histological consistency, can aid in accurate identification.
The implications of this research are significant for clinical decision-making and patient management. The development of improved criteria for distinguishing MPLC and IPM has the potential to contribute to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies for patients with multiple lung cancers. Furthermore, by highlighting the role of NGS as an assisting tool in this differentiation process, the study showcases the value of genomic analysis in lung cancer assessment.
This article represents an important contribution to the field of lung cancer research and clinical practice, as it addresses a clinically relevant issue and provides valuable insights into the utilization of NGS for distinguishing MPLC and IPM. The findings have the potential to impact clinical practice, improve patient outcomes, and pave the way for further research in this area."
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
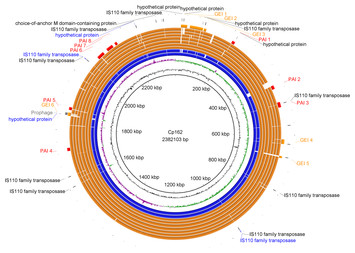
30 January 2024
Resequencing and characterization of the first Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis genome isolated from camel
"-"
 Theerapong Krajaejun, Handling Editor
Theerapong Krajaejun, Handling Editor
 Theerapong Krajaejun, Handling Editor
Theerapong Krajaejun, Handling Editor
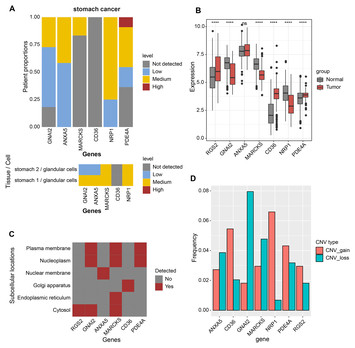
22 January 2024
Single-cell data revealed CD14-type and FCGR3A-type macrophages and relevant prognostic factors for predicting immunotherapy and prognosis in stomach adenocarcinoma
"This article is important because it addresses the significant challenge of tumor heterogeneity in stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD) and explores the potential of single-cell sequencing technology to identify characteristic cell types. The identification of critical cell types and relevant gene modules in tumor progression provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying STAD. Additionally, the construction of a prognostic scoring system and the development of a nomogram based on RiskScore and clinical factors offer a predictive tool for patient survival.
The article's findings have implications for the field of cancer research and clinical practice. By uncovering a single-cell atlas for STAD patients, this study contributes to our understanding of the cellular landscape of this highly heterogeneous tumor. The identification of prognostic factors and their association with patient outcomes allows for more tailored treatment strategies and improved patient care.
Furthermore, the positive feedback to immunotherapy observed in patients with low RiskScore suggests that the identified macrophage gene signature has potential implications for immunotherapeutic approaches in STAD. This finding may have a significant impact on the development of targeted therapies and personalized treatment options for STAD patients.
Overall, this article makes important contributions to the field by advancing our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying STAD and providing potential prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. It has the potential to shape future research directions and improve clinical outcomes for STAD patients."
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
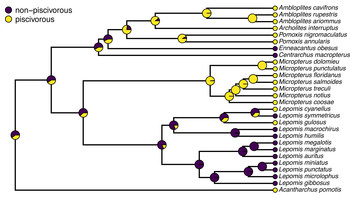
5 January 2024
phytools 2.0: an updated R ecosystem for phylogenetic comparative methods (and other things)
"Although technically about a piece of describing software, this paper doesn't just go the extra mile beyond "normal" software papers, but instead finds a sweet spot between very thorough documentation for users, showcasing sophisticated data science, and illustrating avenues for new discovery. It will go a long way towards both enabling and encouraging comparative phylogeneticists to do and discover great things."
 Hilmar Lapp, Handling Editor
Hilmar Lapp, Handling Editor
 Hilmar Lapp, Handling Editor
Hilmar Lapp, Handling Editor
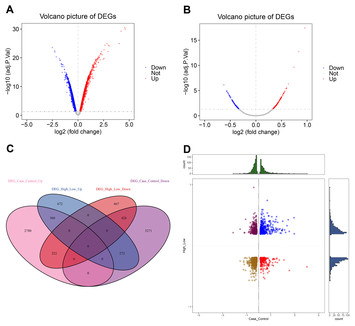
13 December 2023
CXCL10-based gene cluster model serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker for premature ovarian failure
"This study explores the diagnostic potential of Cxcl10 in Premature Ovarian Failure (POF). By employing advanced statistical and machine learning methods, such as ROC curve analysis and LASSO regression, the study provides a comprehensive evaluation of Cxcl10's diagnostic efficacy. The findings could significantly enhance the current diagnostic tools for POF, leading to earlier detection and intervention."
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
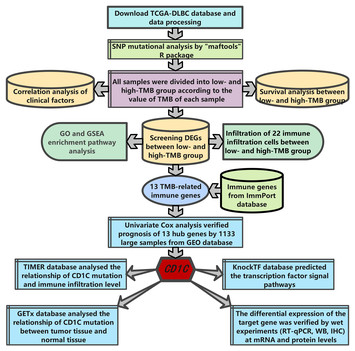
11 December 2023
Identifying CD1c as a potential biomarker by the comprehensive exploration of tumor mutational burden and immune infiltration in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
 Nitin Amdare, Handling Editor
Nitin Amdare, Handling Editor

6 December 2023
Pharmacoscreening, molecular dynamics, and quantum mechanics of inermin from Panax ginseng: a crucial molecule inhibiting exosomal protein target associated with coronary artery disease progression
"This study elucidates the pivotal role of exosomes from epicardial adipose tissue in the progression of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) by identifying SMAD2 as a potential protein target, linked with critical pathways like PI3K-Akt signaling. It leverages a systems biological approach, combining differential gene expression, protein network construction, and functional enrichment, and performs in-depth computational analysis, including ADME screening and molecular dynamics simulations, to assess the inhibitory potential of Panax ginseng-derived compounds on SMAD2. Inermin, a phytochemical, demonstrated significant affinity and stability with SMAD2, suggesting its potential efficacy in managing CAD. This multifaceted approach not only enhances our understanding of the role of exosomes and associated proteins in CAD but also sets a precedent for utilizing innovative methodologies and natural compounds in drug discovery, potentially leading to the development of novel therapeutic strategies and drugs. The findings can have far-reaching implications in providing more effective and targeted interventions for CAD and other cardiovascular diseases, contributing to advancements in cardiovascular research, pharmaceutical research, and clinical practices."
 Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
 Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
67,240 Followers