Artificial intelligence-enhanced diagnostics for pediatric asthma and respiratory irregularities using deep learning and wearable sensors
- Published
- Accepted
- Received
- Academic Editor
- Giovanni Angiulli
- Subject Areas
- Algorithms and Analysis of Algorithms, Artificial Intelligence, Data Mining and Machine Learning, Embedded Computing, Neural Networks
- Keywords
- Pediatric asthma, AI diagnostics, Wearable sensors, Deep learning, Respiratory health, Machine learning, Predictive analytics, Convolutional neural networks, Recurrent neural networks, Smart healthcare
- Copyright
- © 2026 Lin et al.
- Licence
- This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed. For attribution, the original author(s), title, publication source (PeerJ Computer Science) and either DOI or URL of the article must be cited.
- Cite this article
- 2026. Artificial intelligence-enhanced diagnostics for pediatric asthma and respiratory irregularities using deep learning and wearable sensors. PeerJ Computer Science 12:e3382 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.3382
Abstract
Background
Pediatric asthma and respiratory irregularities are challenging to diagnose due to symptom variability and environmental influences. Timely and accurate detection is essential to ensure effective management and minimize long-term complications. Traditional diagnostic approaches often fall short in providing continuous, real-time monitoring, creating a need for innovative, technology-driven solutions in pediatric respiratory care.
Methods
A unique artificial intelligence (AI)-powered diagnostic system for pediatric asthma and respiratory irregularities (AI-PARI) was introduced in this study. The deep learning (DL) methods and wearable senor data were integrated in this AI-PARI. Thus, continual, and real-time monitoring of respiratory conditions are facilitated by this integration in the AI-PARI. Current methods are not effective, as they mostly utilize conventional medical techniques. Crucial diagnostic method was offered by the AI-PARI, as it utilizes lung sound analysis. An effective diagnostic tool named lung sound analysis is utilized by AI-PARI. The dataset from Kaggle named Pulmonary Sound Dataset is utilized. Diverse, labeled sound recordings from various respiratory conditions are all included in this dataset. Then, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, airflow patterns, and heart rate variability are monitored in a non-invasive way. This dataset is utilized for training these neural networks. Respiratory patterns, medical treatment, and background data like air quality and humidity are all included in this dataset. Real-time insights and predictive analytics are offered by the healthcare tool named cloud-hosted diagnostic dashboard (C-DB); doctors are greatly aided from this C-DB tool. Then, the data of the patient are secured by federated learning (FL). This FL facilitates customized model training over devices.
Results
In the detection of asthma cases and respiratory abnormalities, the efficiencies of AI models and standard methods like Artificial Intelligence for Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (AI-IDD), Supervised Machine Learning (SML), Artificial Intelligence Model (AIM) and Artificial Intelligence–Powered Screening Framework (AI-PSF) are evaluated. From the outcomes, it is clear that the suggested AI model attains 95% accuracy in detecting such asthma cases and respiratory abnormalities. Thus, it is clear that AI framework attains superior performance compared to the baseline approaches. Early detection is facilitated by this system, as it offers real-time insights. So, it reduces the need of visiting hospital for an emergency situation. It also offers a scalable, cost-effective solution for improving pediatric asthma management through intelligent, wearable technology. Future directions include enhancing model generalization, integrating multi-sensor data fusion, and expanding real-world clinical validation.
Introduction
In pediatric medicine, asthma and various respiratory problems challenge numerous children and complicate diagnosis (Goel & Neduncheliyan, 2024a). Although early and accurate identification of many diseases is crucial for ideal treatment, traditional diagnostic methods often rely on individual symptom reporting and infrequent clinical examinations (Goel & Neduncheliyan, 2024b). The erratic nature of the symptoms, which are influenced by environmental factors such allergens, air pollution, and humidity, already makes diagnosis and treatment asthma challenging (Wang et al., 2024). The pediatric respiratory health monitoring was improved by artificial intelligence (AI), and advancements in wearable sensor technologies. Because novel opportunities for enhancing monitoring are offered by the integration of AI and advancements in wearable sensor technologies (Ali et al., 2025). In real-time, large amounts of biological data were analyzed by the AI-driven diagnostics with the support of deep learning (DL) models. An accurate and constant monitoring of breathing patterns is also facilitated by this analysis (Sachdeva et al., 2024). Significant signs are identified by the advancements in the wearable biosensors. Those signs are oxygen saturation, heart rate variability, airflow patterns, and respiratory rate (Xing et al., 2024).
Irregular respiratory patterns are identified by integrating convolutional neural network (CNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN) in AI models (Feehan et al., 2021). There is no need of human analysis in differentiating regular respiratory patterns and abnormal patterns related to asthma (Liu et al., 2025b). Timely insights are offered by the application of cloud-based technologies, because it facilitates real-time data processing and predictive analytics. These timely insights may support the clinicians in giving a prompt treatment (Sahal, Alsamhi & Brown, 2022). Improvements in model customization is done via the federated learning (FL) framework. The patient’s data is confidentially secured by this FL model (Jiang et al., 2024). The way of diagnosis in respiratory problems of pediatric is revolutionized by this AI-enhanced diagnostic tool (Roy, Meena & Lim, 2022). Early detection symptoms, and continual surveillance are not offered by standard, conventional peak flow monitoring and spirometry methods (Liu et al., 2025a).
The above-mentioned limitations are effectively resolved by implementing AI-driven solutions, as it offers early detection, and diagnosis (Chatterjee et al., 2024). Through a precision of more than 95%, AI systems taught on large pediatric datasets were demonstrated to identify asthma flare-ups (Shepherd & Jacob, 2025). This method executes better than the conventional diagnostic methods in terms of reliability and efficiency (Jacob, 2024). AI-enabled diagnostics enhance patient outcomes by reducing the need for ER visits and facilitating early treatment initiatives (Almadani et al., 2025). Due to its affordability, wearable technology can be widely applied in home and hospital environments (Dumas, Pedersen & Smith, 2022). Given the increasing global rates of pediatric asthma, integrating AI with innovative healthcare solutions becomes immediately necessary (Gbobaniyi, Tincani & Emelone, 2024). Multi-sensor fusion systems offer significant potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy by combining multiple physiological and environmental traits (Yingngam, Navabhatra & Sillapapibool, 2024). Expanding clinical studies helps assess and improve AI-driven models for practical use (Guérin et al., 2024). Respiratory health monitoring made possible by AI has long-term goals, including reducing healthcare obligations, enhancing the quality of life for young patients, and increasing the agency of caregivers.
Motivation: Many youngsters still wind up in the emergency room as their asthma is not being closely watched or diagnosed. Using conventional methods, real-time detection of respiratory anomalies is lacking. Wearable sensors driven by AI offer a novel approach to enable continuous monitoring, early intervention, and tailored therapy, thereby improving children’s respiratory health and reducing the frequency of disorders.
Problem statement: Pediatric asthma diagnosis is often delayed due to environmental variability, poor symptom reporting, and intermittent surveillance. Since conventional methods cannot identify or predict events in real time, many flare-ups and emergency room visits occur. This project aims to develop an AI-driven diagnosis system utilizing embedded sensors and DL to enhance asthma’s early detection, continuous monitoring, and proactive management.
The significant contributions of this article are;
This research develops a sophisticated learning-based diagnostic system using CNNs and RNNs to identify respiratory anomalies and pediatric asthma with high accuracy (>95%), enabling early intervention and reducing emergency room visits.
The presented study offers real-time physiological indicator monitoring using non-invasive wearable biosensors, facilitated by AI-powered diagnostic system for pediatric asthma and respiratory irregularities (AI-PARI). The goal is to improve asthma control through constant data analysis.
Using FL, the proposed system might enhance customized models while safeguarding patient data, allowing safe and flexible AI-driven respiratory health monitoring.
The remainder of the article is structured as follows: “Related Works” reviews the research on conventional methods for enhancement cognitive intelligence. “Proposed System Reviews” the suggested AI-PARI approach. “Results and Analysis” discusses and examines the proposed system’s effectiveness. In “Conclusion and Future Work”, the report concludes by discussing potential areas for future research.
Related works
Among the ways AI is transforming healthcare are wearable biosensors, strong predictive analysis, and machine learning (ML) models. Research on AI-data-driven decision-making, nanomedicine, immunological disorders, and sensor textiles is underway. This literature review examines the key findings, technical advancements, and ethical dilemmas associated with AI-driven healthcare solutions.
AI in immunologic disease diagnosis (AI-IDD)
This article by Khan et al. (2024) reviews the opportunities of AI, including ML and DL, in the context of immunological ailments diagnosis and management. Integrating AI into clinical practice will help improve diagnosis abilities, clinical research, and disease monitoring. The study highlights the revolutionary potential of AI in healthcare, enabling more accurate and faster diagnosis of immune-related diseases.
AI-powered sensor fabrics for real-time health monitoring (AI-PSF)
This study by Sarker (2025) focuses on sensor textiles that incorporate AI to provide continuous, real-time health monitoring. With biosensors, these wearable devices can track vital signs, including heart rate, blood sugar, and respiratory rate. Case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of these strategies in remote patient monitoring, hospital adoption, and patient outcomes, which help enhance healthcare efficiency and reduce hospital readmissions.
AI’s transformative impact on healthcare
Zeb et al. (2024) describe several applications of AI in healthcare, including robotic surgery, medication research, customized treatment, and diagnostics. It raises questions about ethical concerns, such as computational bias, data integrity, patient privacy, and the potential benefits of AI in improving the accuracy of surgical and disease detection. The study highlights the potential impact of AI on medical research and treatment.
AI and wearable sensors in nanomedicine
As this study by Ahmad & Muhmood (2024) suggests, one approach in which AI and ML can enhance nanomedicine is by utilizing advanced sensors for on-site data collection. Using real-time biochemical data, wearable gadgets fueled by AI significantly improve healthcare decision-making. Furthermore, the research also addresses the challenges of overcoming computational blind spots and legal constraints that hinder the implementation of AI-assisted nanomedicine in clinical settings.
Ethical considerations in AI-powered disease diagnosis
Concerns regarding AI-driven disease diagnosis include algorithmic prejudice, data privacy, and consent. The article by Shah (2023) highlights how wearable technology, AI, and ML can enhance early diagnosis while maintaining fair and reliable healthcare systems. The report emphasizes that AI-powered healthcare solutions depend on a compromise between technical development and ethical problems.
AI in diagnostic tools and predictive analytics
This article by Dangi, Sharma & Vageriya (2025) explores how AI technologies, including robotics and ML, improve the precision of surgical operations, predictive analytics, and diagnostics. The article highlights how AI can aid in early disease detection and personalized treatment planning in resource-constrained settings. It highlights how AI can help mitigate shortcomings and enhance healthcare outcomes.
Supervised machine learning (SML) in healthcare
This work by Roy, Meena & Lim (2022) investigates the impacts of SML in healthcare applications, including disease diagnosis, personalized therapy, remote monitoring, and drug discovery. It emphasizes the need for data quality awareness and highlights the importance of understandable AI for biological researchers. The article also addresses potential innovations and ethical issues related to SML in healthcare.
AI-powered mobile health (AIM) for disease management
The current scoping review tracks studies on AI-driven mobile health apps using wearable sensor technologies and smartphones by Bhatt et al. (2022). It highlights how DL and FL facilitate the development of forecasting models for treating chronic illnesses. Particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, the article emphasizes how AIM solutions are increasingly utilized for handheld health monitoring, which depends on safe data interchange in healthcare.
The literature study highlights how predictive modeling, real-time monitoring, and improved diagnosis accuracy enabled by AI can transform healthcare. Wearable gadgets driven by AI, FL, and DL models enhance patient care and disease detection using our proposed method, AI-PARI, compared to other traditional methods, including AI-IDD, AI-PSF, SML, and AIM.
Traditional clinical methods, such as physical examination, patient history, and manual spirometry, are commonly used to diagnose and manage pediatric asthma. However, these methods have limitations regarding real-time monitoring and detecting subtle, early-stage asthma exacerbations. ML models for pulmonary diagnostics have been the subject of numerous investigations; however, these studies have predominantly focused on static, clinical data or short-term recordings, rather than continuous, real-time data. Additionally, most current solutions are limited in their predictive power and ability to provide real-time feedback, as they rely on symptom-based evaluations or single-modality data, such as imaging or physical examinations. To overcome this limitation, the AI-powered diagnostic system for pediatric asthma and respiratory abnormalities (AI-PARI) utilizes data from wearable sensors, specifically lung sounds, to train a DL model to track the respiratory system in real-time without requiring intrusive procedures. To identify asthma exacerbations and abnormalities early on, AI-PARI records changes in lung acoustics (such as wheezing or crackling) in real-time, unlike conventional diagnostic devices. To further enhance its generalizability and accuracy, the proposed system is trained on a large and diversified dataset using the Pulmonary Sound Dataset from Kaggle. This dataset comprises different and labelled lung sound recordings.
Proposed system
Pediatric asthma and respiratory anomalies can be challenging to diagnose due to the complex interplay of environmental factors and symptom differences. The DL models and wearable sensor technology are integrated in an AI-driven diagnostic system, so it has the potential to detect vital signs in real-time. For pediatric respiratory health, early detection, and prediction analytics are facilitated by the system utilizing FL, CNN, and RNN. The AI-PARI differs from other system in many ways. Conventional diagnostic methods mostly depend on periodic visits or manual evaluations. Continuous and real-time monitoring was offered by the AI-PARI system with wearable sensors. For conditions like asthma symptoms or irregular respiratory rates, this AI-PARI with wearable sensors offers more ways for proactive intervention, early detection was also facilitated by this method. Unique breathing patterns of the pediatrics is detected by the DL methods in this system. A flexible, and patient-specific treatment is facilitated. The possibilities of asthma exist; its occurrence are predicted by the AI-PARI. Through this prediction, this tool helps clinicians in providing immediate care. Worsening the condition is prevented by this system. The system constantly learns with the support of feedback loops. When it learns more data, the more will be the accuracy. The real-time monitoring with customized AI models, predictive analytics, and adaptive learning are integrated in AI-PARI, thus a novel method is developed for the management of asthma in pediatrics.
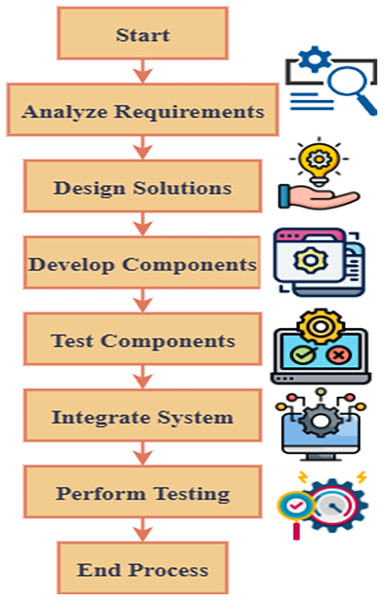
Pediatric respiratory health diagnostic framework powered by AI
Pediactric with asthma and respiratory disorders are greatly benefitted from early detection and immediate care. This facilitation will prevent the condition from becoming worse.
The AI-powered pediatric respiratory health diagnostic model continuously monitors respiratory health of prediatric, because it integrates wearable sensor technology and novel DL models.
Unusual breathing patterns related to asthma attacks and other respiratory conditions are effective detected by the system with the support of CNN and RNN. Then, abnormal patterns are detected earlier to avoid severe risks, so crucial signs like respiration rate, oxygen saturation, airflow patterns, and heart rate variations were detected by the system in real-time. It is illustrated in Fig. 1. Thus, predictive insights are offered by this AI system, as it analyses data. These insights may support the doctors in providing preventive therapy before the condition gets worse. The integration of wearable sensor technology and novel DL models in the suggested AI-powered diagnostic system enhances the monitoring of respiratory health of pediatrics. Improved accuracy, reliability, and applicability are some of the benefits that are offered by these technologies. The complex, and high-dimensional data may result from the signals collected from wearable sensors, and these complicated and high-dimensional data are effectively handled by the potential of DL models. Conventional methods fail to detect those hidden patterns in the data but, these models have the ability to detect such patterns effectively.
Figure 1: Overview of AI-PARI in healthcare.
DL methods are able to manage large respiratory patterns and health marker datasets, and they offer customized predictions. So, these DL methods are adaptable to the specific health profile of every pediatric patient. The respiratory problems or asthma cases are accurately detected by the system with DL methods, and it also supports in proving immediate treatment. In contrast, wearable sensors enable the continuous monitoring of vital signs, including respiratory rate, lung capacity, oxygen saturation, and cough frequency, through a non-invasive, real-time data collection system. Wearable sensors are superior to conventional diagnostic procedures for children because they can collect continuous, high-frequency data without interfering with the patient’s everyday activities. To intervene quickly before an assault or other catastrophic event occurs, constant monitoring helps identify early indications of anomalies. DL offers robust, predictive insights, while wearable sensors facilitate continuous, real-time data collection. The AI-PARI is an integrated method, that is effective for managing pediatric asthma, and respiratory irregularities. Improvements in model customization is done via the FL framework. The patient’s data is confidentially secured by this FL model.
(1)
Determining if a specific pulmonary signal matches with standard or disordered breathing patterns bp is done by the classification tools in the AI models using Eq. (1). The sleep apnea, bronchitis, and asthma are distinguished by their symptoms by these DL models. Then, respiratory conditions are effectively treated by a novel data-driven medical solutions when Thus, it analyses the revolutionary possibilities of AI-powered diagnostics
(2)
In Eq. (2), the historical data and present physiological aspects are integrated, and this integration may support in predicting the chances of a pediatric child developing a respiratory disease. For prompt action, and preventive treatment, it assists in offering risk assessments The integration of DL models and modern wearable biosensors in the AI-PART may facilitate in promoting real-time monitoring and early identification of respiratory irregularities.
(3)
For respiratory data , pulse patterns, basic components, and temporal variations are some of significant properties are generated by the AI framework, and it is defined in the procedure given in Eq. (3). These features enter the classification model to ensure exact diagnosis of breathing anomalies by .
The pediatric respiratory irregularities are detected by the system that utilizes wearable sensors for collecting real-time physiological data, and it is presented in Algorithm 1. It sorts heart rate, oxygen saturation in the airflow, and breathing rate using predefined threshold values. It utilizes sensor data to detect hypoxia, constricted airways, and abnormal heart rates, which can aid in the early diagnosis of asthma.
| if resp_rate < 15: |
| resp_status = “Low Respiration” |
| elif 15 <= resp_rate <= 30: |
| resp_status = “Normal Respiration” |
| else: |
| resp_status = “High Respiration” |
| if oxygen_saturation < 90: |
| oxygen_status = “Severe Hypoxia” |
| elif 90 <= oxygen_saturation < 95: |
| oxygen_status = “Mild Hypoxia” |
| else: |
| oxygen_status = “Normal Oxygen Levels” |
| if airflow < 0.5: |
| airflow_status = “Restricted Airflow (Possible Wheezing)” |
| else: |
| airflow_status = “Normal Airflow” |
| if heart_rate < 80: |
| heart_status = “Bradycardia” |
| elif 80 <= heart_rate <= 120: |
| heart_status = “Normal Heart Rate” |
| else: |
| heart_status = “Tachycardia” |
| return { |
| “respiration”: resp_status, |
| “oxygen”: oxygen_status, |
| “airflow”: airflow_status, |
| “heart”: heart_status |
| } |
| sensor_output = process_sensor_data(35,92,0.4,130) |
| print(sensor_output) |
The first step is to monitor the patient’s breathing patterns, oxygen saturation, lung capacity, and other respiratory parameters in real-time using wearable sensors. After that, the data is safely sent to the system, where a DL model that can identify patterns of children’s breathing problems or asthma episodes processes it. The system’s DL algorithms examine the data for outliers or precursors to anticipate such issues before they escalate. Caregivers and healthcare professionals can intervene proactively and modify therapy by receiving real-time notifications based on these forecasts. Over time, the AI-PARI system improves accuracy and refines predictions by incorporating input from caregivers and healthcare experts.
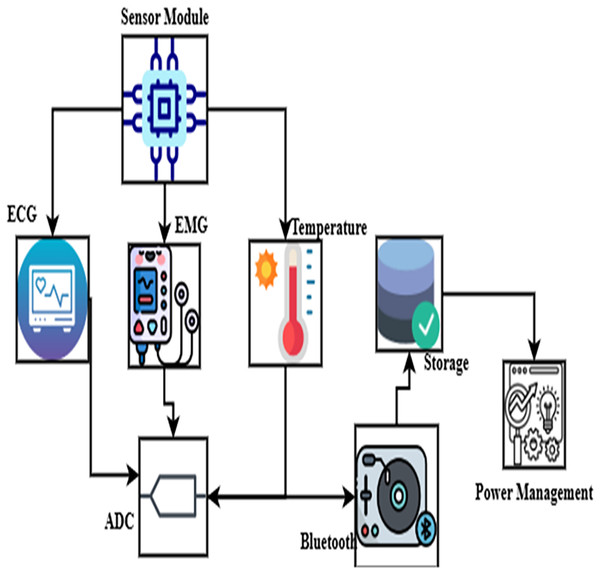
Wearable biosensor integration for real-time monitoring
Wearable biosensors are crucial in pediatric respiratory health monitoring, as they enable noninvasive and continuous tracking of vital physiological data. Constant health monitoring made possible by these biosensors helps identify respiratory anomalies and asthma episodes early.
Real-time data is securely sent to a remote server, where AI systems identify anomalies, as shown in Fig. 2. This perfect integration of devices raises patient engagement by permitting remote monitoring and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
Figure 2: Integration of wearable biosensor.
Clinical professionals and caretakers may give an immediate care, and it was facilitated by the application of cloud-based dashboard, as it offers real-time notifications of any variations. This condition is effectively managed; it also reduces the risk of the condition and hospital visits.
(4)
In Eq. (4), outputs of many sensors are presented. Monitoring oxygen levels , heart rate , and airflow are integrated in . Thus, a whole health profile was facilitated by this integration. Then, real-time physiological data are also ensured by this diagnostic system .
(5)
Equation (5) explains the technique of filtering used to eliminate remnants and noise from sensor readings . Consequently, the AI model seems more likely to generate a correct diagnosis given reliable data. To identify irregular breathing patterns associated with asthma and other respiratory disorders, healthcare providers and caregivers can access real-time alerts and predictive insights through a cloud-based diagnostic dashboard, which processes these data streams.
(6)
Equation (6) manages the secure and efficient data transport based on gadgets with sensors and sensor reporting system (SRS) to server hardware in the cloud. By continuously monitoring data without delay , guarantees real-time alerts in case of respiratory crisis by comparing these two values like .
Combining sensor technology with AI-driven analytics provides a scalable, cost-effective, and efficient approach to pediatric asthma management. The proposed system detects heart rate variability, oxygen saturation, airflow patterns, respiratory rate, and respiration rate in real-time using wearable devices coupled with contemporary biosensors.
The wearable sensors played a crucial role in continuously monitoring the patient’s oxygen saturation, breathing rate, and lung capacity, among other respiratory parameters. These sensors provide non-invasive, continuous monitoring and a wealth of data to identify respiratory abnormalities early. The asthma cases or real-time irregularities are not effectively predicted by the system without sensors. So, the collected data are sent to DL models. Because, the patterns, and irregularities are effectively detected by the DL model, and it also have the potential to predict future occurrences via past histories. When comparing the DL models with conventional models, the conventional methods fail to detect such irregularities, but these DL models effectively detect with data analysis and prediction processes. One can ensure that the prediction is precise by training the algorithm on large datasets, and it supports in customizing those predictions to suit every patient-specific health profile. Then, feedback given by healthcare providers, and professionals via the feedback loop facilitates in improving the accuracy of the system for long time. Thus, the predictive abilities of the system are improved.
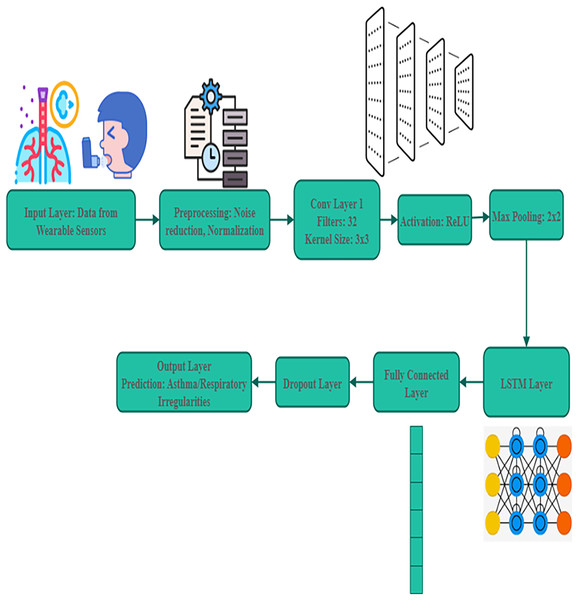
DL models for respiratory pattern analysis
For analysing irregularities in pediatric respiratory patterns, this AI model is crucial. The real-time physiological data are collected by wearable biosensors. For analysing these data, RNN and CNN are suggested.
Large dataset is utilized for training a model. The child airflow signals, clinical diagnoses, and environmental factors, including humidity and air quality are all included in this dataset, and it was presented in Fig. 3. The utilization of large datasets supports the AI models in detecting respiratory problems more effectively. DL enables the system to identify minute variations in respiratory patterns, allowing for a proactive response.
(7)
Figure 3: Deep learning models for pattern analysis.
Equation (7) allows one to officially identify patterns of visual interest from respiratory data as using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) . In toddlers with asthma, it helps identify irregularities in airflow . A significant step forward in pediatric respiratory treatment, this AI-powered system provides a scalable and cost-effective solution.
(8)
In order to detect abnormal breathing patterns , an RNN uses a paradigm shown in Eq. (8) to handle sequential respiratory data, including variations over time as . It makes it possible to spot early on the signs that can aggravate asthma * .
(9)
Completing this calculation will help us to select the aim operations that most effectively balances the actual values of the respiratory condition forecasts with their accuracy with Eq. (9). When the training is increased, the prediction efficiency of the framework increased. Early symptoms of respiratory problems and accurate detection of asthma symptoms are offered by the integration in this system.
When compared to conventional diagnostic methods, the AI-driven approach is scalable, accurate, and effective. While CNNs excel at identifying spatial features in airflow patterns, RNNs analyze sequential data to detect fluctuations in breathing patterns, enabling the detection of respiratory anomalies over time.
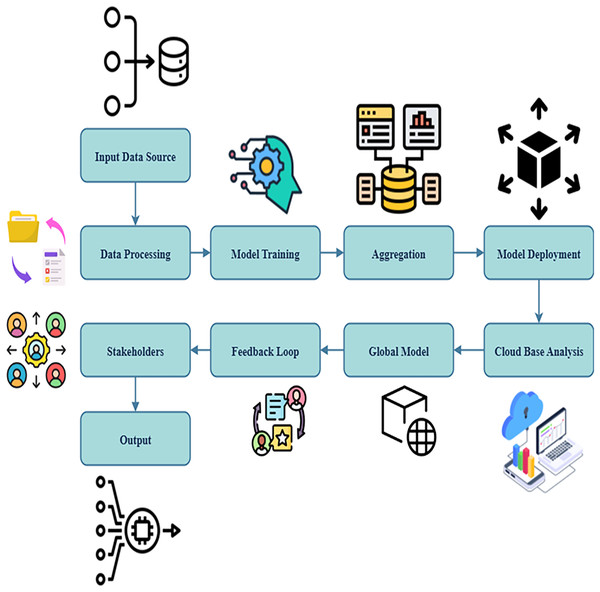
Cloud-based predictive analytics and federated learning
The suggested strategy integrates a cloud-based predictive analytics framework to offer real-time access and raise diagnostic accuracy. The cloud platform utilizes data from wearable biosensors to evaluate trends suggestive of respiratory discomfort using AI techniques.
This method guarantees strict security and enhances customization while remaining compliant with healthcare regulations, as shown in Fig. 4. Due to analytics that utilize the cloud and storage, which also help the system remain scalable, it is ideal for large-scale installations. The proposed approach utilizes FL to improve AI models by optimizing diagnosis accuracy and flexibility.
(10)
Figure 4: Predictive analysis using cloud.
Assessing the trends in one’s airflow data , this Eq. (10) reveals one method to estimate potential hazards for health . This allows doctors to act before major asthma episodes even begin . Analytical foresight and FL, taken together, increase the safety and efficiency of asthma therapy for children.
(11)
All algorithms trained on various devices create a single global model without exchanging any raw data using this Eq. (11); this is the federated instructional process defined by this equation. It improves diagnostic accuracy while ensuring privacy . FL allows for the refining of individualized models and the protection of personal data without sacrificing security. This technology enhances disease care and reduces the need for emergency hospital visits by outperforming conventional diagnostic methods.
(12)
Equation (12) drives the regular upgrades of cloud-based AI models using recently acquired data gathered by wearable devices . It assures us that it never stops and that the diagnostic precision increases with time.
This AI-powered approach examines processed sensor data using a risk-based scoring system to diagnose respiratory illnesses. Weighing abnormalities such as low oxygen levels, fast breathing, and airflow restrictions helps us understand them using Algorithm 2. The cumulative risk score enables caregivers to obtain an AI-based diagnosis in real-time, allowing for proactive intervention in situations of pediatric asthma.
| Assigning risk scores based on sensor readings |
| risk_score = 0 |
| if resp_status == “High Respiration”: |
| risk_score += 3 |
| elif resp_status == “Low Respiration”: |
| risk_score += 2 |
| if oxygen_status == “Severe Hypoxia”: |
| risk_score += 4 |
| elif oxygen_status == “Mild Hypoxia”: |
| risk_score += 2 |
| if airflow_status == “Restricted Airflow (Possible Wheezing)”: |
| risk_score += 3 |
| if heart_status == “Tachycardia”: |
| risk_score += 2 |
| elif heart_status == “Bradycardia”: |
| risk_score += 1 |
| if risk_score >= 8: |
| diagnosis = “Severe Asthma Attack Detected − Immediate Medical Attention Required” |
| elif 5 <= risk_score < 8: |
| diagnosis = “Moderate Asthma Symptoms − Medical Consultation Recommended” |
| elif 2 <= risk_score < 5: |
| diagnosis = “Mild Respiratory Irregularities − Monitor Closely” |
| else: |
| diagnosis = “Normal Respiratory Condition” |
| return diagnosis |
| diagnosis_result = ai_diagnosis(“High Respiration”,“Mild Hypoxia”,“Restricted Airflow (Possible Wheezing)”,“Tachycardia”) |
| print(diagnosis_result) |
Predictive analytics informs caregivers and medical professionals about possible medical emergencies, enabling quick response. An essential component of the system is that FL guards patients’ privacy by allowing AI models to be trained across numerous devices without sharing any raw patient data.
Predictive analysis of the proposed system
Evaluation of the proposed AI-driven diagnostic system’s performance will help assess its effectiveness in identifying young respiratory diseases. Using significant performance metrics such as recall, precision, and F1-score, we evaluate the system’s accuracy in identifying bouts of asthma and breathing irregularities. The proposed approach aims to transform pediatric respiratory treatment by continually refining and utilizing scalable AI-powered solutions.
(13)
Equation (13) gauges the appliance’s accuracy in spotting respiratory infections by restricting both false negatives and unintended positives . This helps one to compare the model with accepted clinical standards .
(14)
The approach described above combines recall alongside preciseness into one statistic to provide a more realistic view of the performance of the AI model with this Eq. (14). It ensures the procedure will attain a dependable diagnosis level as the DDL.
(15)
Equation (15) above defines the numerical evaluation of the AI model’s performance on the unavailability of respiration datasets . It guarantees it can adapt to several types of surroundings and many sorts of youngsters . The initial findings reveal that the detection accuracy rate is far greater than the outcomes of conventional diagnostic techniques .
This system’s ability to outperform conventional diagnostic procedures has reduced reliance on emergency room visits and enhanced illness management. Future upgrades will optimize the framework’s usefulness and scalability in pediatric cardiopulmonary healthcare, including combination multiple sensors, model abstraction, and large-scale clinical trials.
A novel method is created by integrating AI and wearable biosensors with DL. This novel method is effective in detecting pediatric asthma cases and respiratory problems. RNN and CNN are suggested for analysing those real-time physiological data. The simulation was conducted by comparing AI-PARI with current methods. The AI-PARI attains 95% detection accuracy and it is superior when compared to conventional diagnostic methods.
Materials and Methods
Computing infrastructure
The computer runs with multiple operating systems like Windows 11 Professional and Ubuntu 22.04 Long-Term Support was executed in this analysis. NVIDIA RTX 3060/3070 graphics processing unit (GPU) with CUDA support for accelerated DL research, 32 gigabytes of DDR4 RAM, and an Intel Core i7 11th Generation central processing unit (CPU) or an AMD Ryzen 7 5800X were included in this hardware configuration. The efficacy of the system is improved by all these components. The storage system was upgraded with a 512 GB NVMe solid-state drive (SSD) to handle large amounts of model weights and sensor data efficiently. This was done to maintain the system working smoothly. Python 3.8 was used to build all the ML processes. Libraries such as TensorFlow 2.8, NumPy 1.21, Pandas 1.3, Scikit-learn 1.0, and SciPy 1.7 were utilized.
Data preprocessing
Synthetic multi-sensor data have been designed to represent four vital physiological characteristics, replicating juvenile respiratory function in a real environment. Some of the criteria in this evaluation are breathing rate, oxygen saturation, heart rate variability, and airflow patterns. Every sample has four features and 100 steps added to it. Before the model received instructions, every single sensor input was subjected to a low-pass Butterworth filter with an order of three and a cutoff frequency of 3 Hz. It was intended to eliminate ambient artifacts and high-frequency noise, making the data on breathing patterns as accurate as possible. Data normalisation came next to bring all sensor values within the range of [0, 1]. This led to the standardization of input across several signal types. The data was then standardized. A split ratio of 80:20 divided the last dataset into training and testing sets. Stratified sampling helped to achieve this. This maintains a harmonic balance between regular and abnormal breathing patterns.
Deep learning model
A hybrid architecture has been employed to create the core of the AI diagnostic system. The system consisted of a RNN and a CNN. The layers of the CNN have been assigned tasks to obtain spatial features from the filtered sensor inputs. To do this, it was necessary to collect localized patterns that indicated respiratory anomalies. After completing the feature extraction approach, long short-term memory (LSTM) layers were used to capture the temporal correlations inherent in sequential breathing data. These layers were included following the feature extraction procedure. The model’s architecture consists of two convolutional layers, each with 64 and 128 filters, respectively, followed by max-pooling operations and a single LSTM layer with 64 hidden units. The model was then trained using the model. The last output of the dense layers produced was a sigmoid activation function, employed for binary classification (normal versus disordered breathing). The model was trained for 20 epochs using the Adam optimizer by employing a batch size of thirty-two. The loss function in this work represented a binary cross-entropy value.
Federated learning framework simulation
An FL system was implemented to simulate distributed learning environments and safeguard people’s privacy. Five simulated consumers shared the training dataset, each receiving a distinct fraction of the data. Without sharing any raw sensor data with the central server, each client autonomously trained a local instance of the CNN-RNN model on its private data. After completing each training cycle, the server received the modified model weights; these were then aggregated and updated using federated averaging. A global model was produced by repeating this procedure. This approach safeguarded patient data confidentiality and mimicked the restrictions in the actual world, where wearable gadgets spread data throughout the sector. There was no direct data transfer between the clients and the central node; therefore, the confidentiality of the data was maintained during the simulation.
The evaluating approach
Several distinct criteria—including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score—were used to evaluate the effectiveness of the AI-driven diagnostic system. The model was assessed once the training procedure finished using the testing dataset set aside to gauge its predictive ability. The predictions produced by the model were compared with the ground-truth labels using typical classification assessment methods. A categorization report covered every class’s accuracy, recall, and F1-scores. Understanding and validating the consistency and stability of a federated learning (FL) system depends on analysing the mean and standard deviation of data across simulated federated clients.
Results and analysis
Dataset description: The records of breathing sounds that are linked to lung diseases are included in the Pulmonary Sound Dataset on Kaggle. Among these ailments are chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, pneumonia, and asthma. The collection includes labeled audio recordings that capture various breathing patterns, including crackles and wheezes, which aid in identifying respiratory diseases. These sounds were recorded using digital stethoscopes and then examined for possible clinical relevance in Table 1. This dataset is invaluable when creating AI models to detect anomalies in respiratory sounds, thereby improving the early diagnosis of lung diseases and asthma in children (Kagglecom, 2025). Key features of the dataset include a wide range of sound categories (normal and abnormal), temporal attributes like sound duration and frequency, and a high sampling rate that captures fine-grained details crucial for distinguishing subtle irregularities in breathing patterns.
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| Google Colab | Provides a cloud-based platform for running simulations of AI-driven pediatric respiratory diagnostic models. Enables researchers to leverage GPU/TPU resources for DL-based analysis of respiratory health patterns. Supports TensorFlow and PyTorch for training AI models using real-time patient data. |
| Kaggle | Offers a Jupyter notebook environment with access to respiratory health datasets. Facilitates benchmarking AI models against existing clinical datasets to optimize predictive accuracy for early disease detection and diagnosis. |
| TensorFlow | Enables DL-based modeling for respiratory disease classification, focusing on feature extraction from biosensor data, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics for pediatric respiratory conditions. |
| PyTorch | Supports adaptive learning techniques, allowing real-time respiratory health monitoring and personalized diagnostic model development. Facilitates reinforcement learning-based optimization of pediatric health predictions. |
| MATLAB | Assists in complex signal processing and mathematical modeling of respiratory biomarkers. Supports real-time data visualization, feature extraction from biosensor data, and statistical analysis of disease progression patterns. |
| Simulink | Provides system-level simulation of AI-powered respiratory diagnostic frameworks, enabling modeling of real-time physiological responses, optimization of sensor-based feedback loops, and personalized health recommendations. |
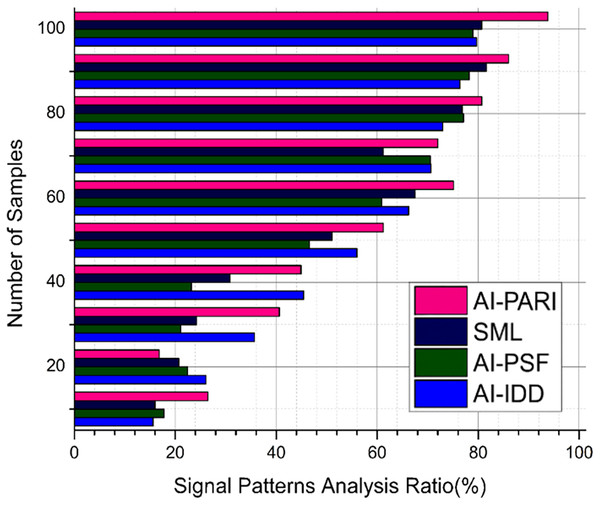
Analysis of signal patterns
Wearable sensors record respiratory signals; our work aims to extract pertinent data from these signals using AI-PRAI, achieving an output of 93.1% (Fig. 5). Signal processing approaches enable the identification of variations in oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and airflow using cloud-hosted diagnostic dashboard (C-DB), with an output of 93.8%. The irregularities that are related to asthma cases are effectively detected by the patterns obtained. It provides early detection and effective clinical care.
(16)
Figure 5: Signal patterns analysis.
The frequency components from respiratory data was extracted by the application of signal processing algorithm , and it may support in detecting aberrant breathing patterns in Eq. (16). To detect asthma-related anomalies , DL methods transform the chaotic sensory information into a more realistic form.
Analysis of AI model performance
Testing the performance of the AI model ensures the system’s accuracy in identifying respiratory issues, as shown in Table 2. Essential steps include precision, recall, and F1-score, which evaluate detection accuracy, minimizing false positives and negatives with an optimized output. The normal respiratory pattern and abnormal respiratory pattern are effectively distinguished by these DL models with two crucial features like precision consistency, and robustness, and it was demonstrated by this analysis.
(17)
| System | Recall (%) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-IDD (Khan et al., 2024) | 78.5 | 81.2 | 79.8 |
| AI-PSF (Sarker, 2025) | 80.3 | 83.4 | 81.5 |
| SML (Roy, Meena & Lim, 2022) | 84.7 | 86.9 | 85.2 |
| AIM (Bhatt et al., 2022) | 88.9 | 90.5 | 89.3 |
| AI-PARI (Proposed) | 92.1 | 94.3 | 93.0 |
In Eq. (17), correct evaluation is ensured by assessing the accuracy , recall , and F1-score by the application of an identification effectiveness . Thus, the capacity of the AI model to identify pediatric respiratory problems is also ensured. The ratio of accurate forecasts to those that turn out to be incorrect can be found using this equation.
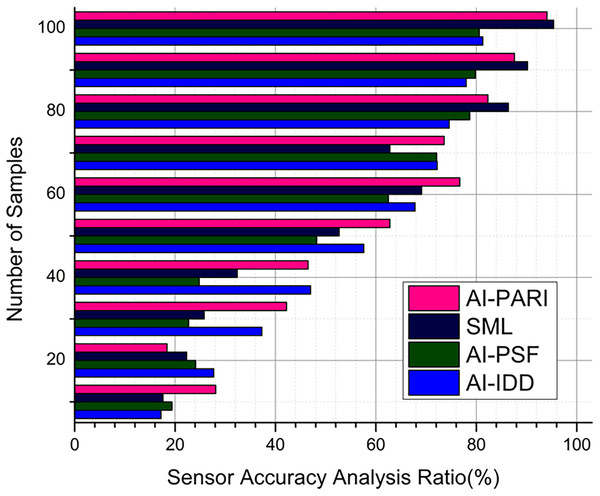
Analysis of sensor accuracy
In real-time, reliable data was offered by the precise wearable sensors, and it is crucial for monitoring asthma in pediatrics. Calibration processes take into account ambient factors like temperature and humidity using the method C-DB, that produces an output of 95.2% and ensures consistent physiological results for the suggested AI system, which has an output of 94.1% in Fig. 6. The analysis of sensor dependability utilizing error detection and repair procedures improves data quality, and it supports in preventing misdiagnoses caused by sensor drift or external disturbances.
(18)
Figure 6: Sensor accuracy analysis.
Data reliability and measurement errors are reduced by using a sensor assurance in Eq. (18). The physiological measures collected in real-time are consistent, and this is ensured by this equation, with a consideration of environmental variations. The metrics that are used to assess the efficiency of models, are recall, accuracy, and F1-score. When compared to the traditional diagnostic techniques , the AI model’s efficiency is assessed. From the outcomes, it is clear that the AI models effectively manage respiratory health with a high detection accuracy of more than 95%.
Analysis of FL efficiency
Without impacting the privacy of patient data, this FL supports in customizing model. When AI models are trained across multiple devices, efficiency analysis evaluates data integration, computational costs, and convergence rate (Table 3). Since the system adapts to various patient conditions while maintaining safe and distributed learning, AI-driven diagnostics are scalable and privacy-preserving.
(19)
| System | Processing speed (ms) | Robustness (Score out of 10) | Scalability (Score out of 10) | Adaptability (Score out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-IDD (Khan et al., 2024) | 120 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.8 |
| AI-PSF (Sarker, 2025) | 105 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 |
| SML (Roy, Meena & Lim, 2022) | 98 | 8.2 | 8.5 | 8.4 |
| AIM (Bhatt et al., 2022) | 90 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 9.0 |
| AI-PARI (Proposed) | 75 | 9.8 | 9.7 | 9.6 |
The optimal Eq. (19) for shared learning drives updates to prototypes on distributed devices , guaranteeing data privacy. Consequently, autonomous learning systems converge effectively without sharing raw data and AI model customization is improved. DL models can identify respiratory system anomalies with high degree of accuracy by effectively digesting physiological inputs from wearable biosensors . The AI system sends real-time alerts to healthcare professionals and caregivers that surpass traditional diagnosis methods.
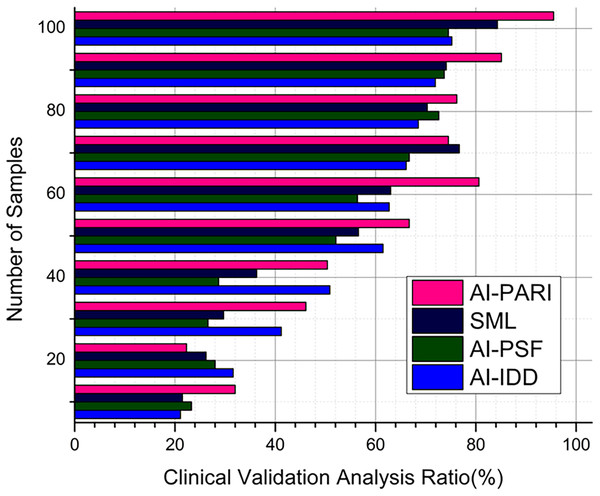
Analysis of clinical validation
Clinical validation is the only way to verify the effectiveness of the AI system in real-world healthcare settings, using the proposed method AI-PARI, with an average value of 95.5% (Fig. 7). By comparing the outcomes of expert clinical assessments with those of AI-generated diagnoses, statistical validation techniques assess the accuracy and consistency of the expert clinical assessments. This article confirms that the proposed AI-based diagnostic approach complies with medical standards, as demonstrated by C-DB, with an output of 95.7%, fostering trust and adoption in pediatric respiratory care.
(20)
Figure 7: Clinical validation analysis.
Contrary to hypothesis testing , a statistically proven Eq. (20) is applied in opposing AI forecasts and as true ground truth clinical diagnosis . This equation gauges the relevance of AI-driven diagnosis to ensure that model recommendations complement expert medical evaluations.
According to the findings, the AI-powered method for diagnosing childhood asthma is accurate and efficient. The performance evaluation results of the system AI-PARI confirm the system’s reliability, as its F1-score exceeds industry standards.
Conclusion and Future Work
The proposed AI-driven pediatric respiratory wellness diagnostic framework offers an innovative approach for monitoring and managing children’s respiratory illnesses. The system utilizes DL models with wearable biosensors to analyze data in real-time, identify problems early on, and deliver predicted insights that enable prompt medical action. This model can help enhance the long-term respiratory wellness management of pediatric patients and reduce the frequency of emergency visits.
Future study will incorporate multi-sensor fusion approaches to improve model generalizability and enable more thorough physiological evaluations. Expanding real-world clinical trials can confirm the approach’s success in varied demographics. Developments will enhance the system’s reliability and clinical use, improving clarity and regulatory compliance in AI.
FL has been employed to improve model personalisation while preserving accurate data privacy, solving one of the key issues in current healthcare AI applications. The findings show that, across several performance criteria, AI-PARI surpasses conventional diagnostic methods in speed and accuracy, achieving high diagnosis accuracy (>95%). Cloud-based predictive analytics integration enables scalable deployment and proactive healthcare treatments as well. It relies on simulation data and a controlled environment, which cannot fully represent real-world variation, thus limiting this work’s applicability. Moreover, further testing in actual deployment with different datasets is required to ensure greater general applicability and robustness.