PeerJ Section
Bioinformatics and Genomics
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 8.1 (view impact metrics).
55,952 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Bioinformatics and Genomics articles 
3 August 2020
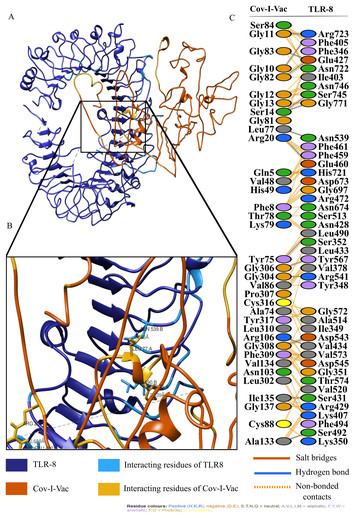
Anti-COVID-19 multi-epitope vaccine designs employing global viral genome sequences
"The topic is highly significant since the only solution to the pandemic seems to be an effective vaccine. The manuscript will surely attract numerous readers."
 Jun Chen, Handling Editor
Jun Chen, Handling Editor
 Jun Chen, Handling Editor
Jun Chen, Handling Editor
21 July 2020
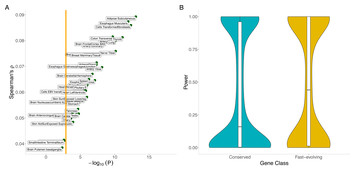
The regulatory genome constrains protein sequence evolution: implications for the search for disease-associated genes
"The paper present a novel approach in assessing tissue-specific impact of gene expression on protein sequence evolution."
 Hossein Khiabanian, Handling Editor
Hossein Khiabanian, Handling Editor
 Hossein Khiabanian, Handling Editor
Hossein Khiabanian, Handling Editor
30 June 2020
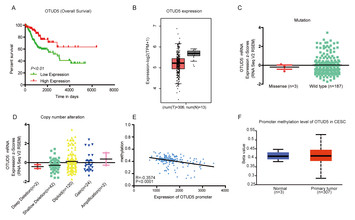
Analysis of deubiquitinase OTUD5 as a biomarker and therapeutic target for cervical cancer by bioinformatic analysis
"In this research paper, the authors analyzed the expression of (ovarian tumor protease) deubiquitinase 5 (OTUD5) in cervical cancer and its relationship with clinical characteristics. This study provided new insights for further research on its regulatory mechanism in tumors."
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
17 June 2020
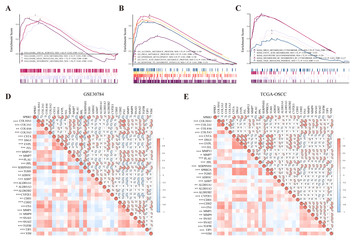
Identification of SPRR3 as a novel diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma via RNA sequencing and bioinformatic analyses
"The work may provide important biomarkers in clinical test."
 Xuehui Huang, Handling Editor
Xuehui Huang, Handling Editor
 Xuehui Huang, Handling Editor
Xuehui Huang, Handling Editor
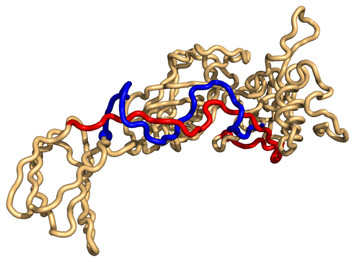
11 June 2020
GISA: using Gauss Integrals to identify rare conformations in protein structures
"The identification of rare conformations in protein structures is a challenging and important task. These conformations are often critical for protein function. This work provide an interesting different way to tackle this problem."
 Elena Papaleo, Handling Editor
Elena Papaleo, Handling Editor
 Elena Papaleo, Handling Editor
Elena Papaleo, Handling Editor
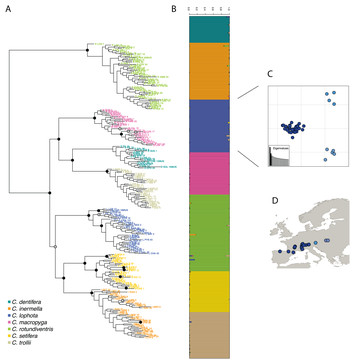
10 June 2020
DiscoSnp-RAD: de novo detection of small variants for RAD-Seq population genomics
"A rapid, efficient and robust tool for analyzing RADseq and other related data. Has the potential to be widely used by the scientific community."
 Tomas Hrbek, Handling Editor
Tomas Hrbek, Handling Editor
 Tomas Hrbek, Handling Editor
Tomas Hrbek, Handling Editor
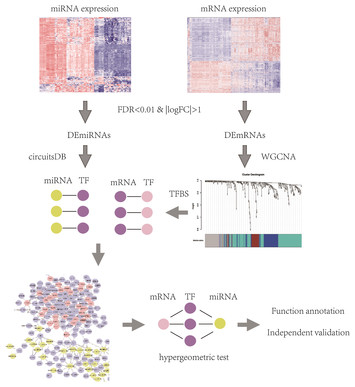
7 May 2020
Integrated analysis of lymphocyte infiltration-associated lncRNA for ovarian cancer via TCGA, GTEx and GEO datasets
"In this study, Wu et al identified long non-coding RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) axes that could delineate more reliable prognostic parameters of high-grade serous ovarian cancer, and to examine the long non-coding RNAs’ possible mechanism of in lymphocyte infiltration. The authors were able to define numerous prognostic biomarkers for the incidence and development of high-grade serous ovarian cancer and constructed a network for ceRNA axes."
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
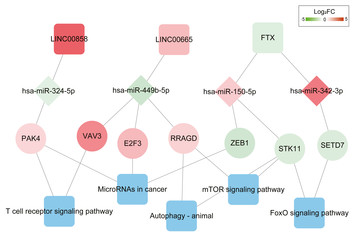
6 May 2020
Identification of key miRNAs in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma using an integrated bioinformatics approach
"Previously studies indicated the association of aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) and transcriptional factors (TFs) with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. In work conducted by Zheng et al., the authors investigated potential transcriptomic markers of hepatocellular carcinoma using the analysis of microarray datasets. They used datasets available in the GEO database. Their analysis indicated that two miRNAs—hsa-mir-106b and hsa-mir-195 are identified as potential classifiers of hepatocellular carcinoma."
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
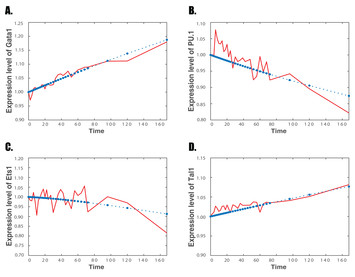
29 April 2020
A non-linear reverse-engineering method for inferring genetic regulatory networks
"In this manuscript conducted by Wu et al., the authors proposed a new method to infer the detailed regulatory mechanisms involved in hematopoiesis. This work focused on the development of a computational approach to investigate the effect of possible protein heterodimers and/or synergistic effects on genetic regulation. In summary, the authors proposed a method that is an effective approach to infer the topological structure and dynamic property of genetic regulations."
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
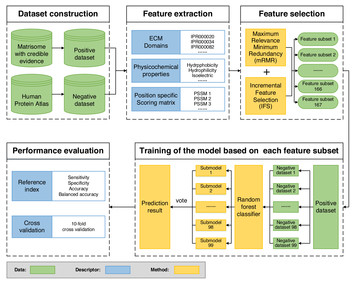
29 April 2020
ECMPride: prediction of human extracellular matrix proteins based on the ideal dataset using hybrid features with domain evidence
"In this work conducted by Liu et al, the authors described the development of a new computational tool to study human extracellular matrix proteins. The authors used experimentally verified extracellular matrix datasets and a machine learning model to develop ECMPride, a flexible and scalable computational tool for predicting extracellular matrix proteins. ECMPride has a number of putative extracellular matrix proteins as well as several biological annotations. This tool might contribute to research focused on the identification of members of this important class of proteins."
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
 Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Walter de Azevedo Jr., Handling Editor
Collections
View all 
German Conference on Bioinformatics 2017 Collection

Practical Data Science for Stats
‘Methods, tools & platforms for Personalized Medicine in the Big Data Era' NETTAB 2017 Workshop Collection.

Endless forms - advances in evolutionary analyses of biodiversity

The SMBE 2017 Collection
55,952 Followers


