PeerJ Section
Bioinformatics and Genomics
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 8.1 (view impact metrics).
55,958 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Bioinformatics and Genomics articles 
24 November 2023
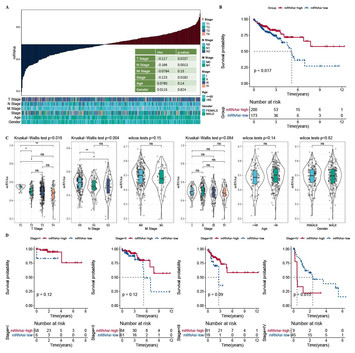
Development of a 5-mRNAsi-related gene signature to predict the prognosis of colon adenocarcinoma
"This study advances the understanding of colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) by developing a prognosis model based on mRNA stemness index (mRNAsi). The researchers identified specific genes correlated with survival rates, clinical stages, and responses to treatments like immunotherapy. By highlighting the connections between these markers and various aspects of the disease, the findings could pave the way for more targeted and effective therapies for COAD, enhancing treatment outcomes."
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
21 November 2023
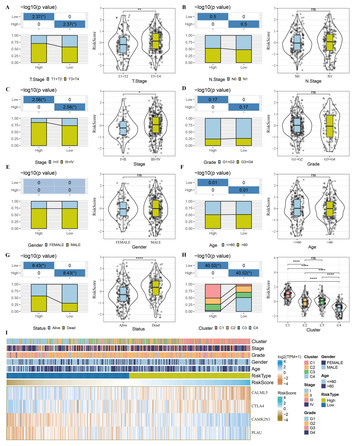
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-specific prognostic signature and drug sensitive subtypes based on programmed cell death-related genes
"This article innovatively reports a prognostic model involved in the development and treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. It is useful for clinical management."
 Zhijie Xu, Handling Editor
Zhijie Xu, Handling Editor
 Zhijie Xu, Handling Editor
Zhijie Xu, Handling Editor
15 November 2023
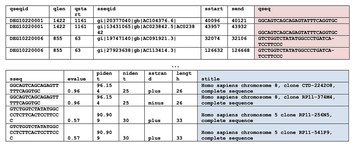
In-silico study of antisense oligonucleotide antibiotics
"This study underscores a significant advancement in the ongoing battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a paramount concern in global health due to the dwindling development of new drugs. By pivoting from the traditional focus on small-molecule antibiotics to RNA-based therapeutics, particularly antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), researchers have paved the way for a novel paradigm in antibiotic design. This research presents a bioinformatics pipeline tailored to identify potent ASO targets within essential bacterial genes, offering an efficient toolset to expedite ASO antibiotic research. By testing the approach on three pertinent bacterial species, the study not only confirms the efficacy of the pipeline but also provides a public database of ASO targets. This is invaluable for future research and holds the potential to significantly impact the development of next-generation antibiotics."
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
28 September 2023
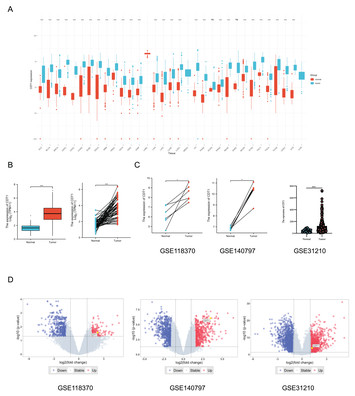
Identification of CDT1 as a prognostic marker in human lung adenocarcinoma using bioinformatics approaches
"The comments of the reviewer is helpful."
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
 Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
Peixin Dong, Handling Editor
15 September 2023
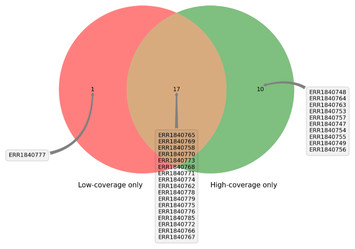
DEVOUR: Deleterious Variants on Uncovered Regions in Whole-Exome Sequencing
"Love the acronym! The functionality of this tool is not only for human disease, as demonstrated in the paper, but also other similar exome studies that seek to understand underlying changes leading to phyenotypic differences."
 Brenda Oppert, Handling Editor
Brenda Oppert, Handling Editor
 Brenda Oppert, Handling Editor
Brenda Oppert, Handling Editor
8 September 2023
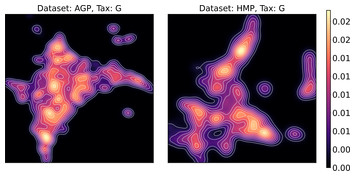
Absence of enterotypes in the human gut microbiomes reanalyzed with non-linear dimensionality reduction methods
 Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
Alexander Bolshoy, Handling Editor
7 September 2023
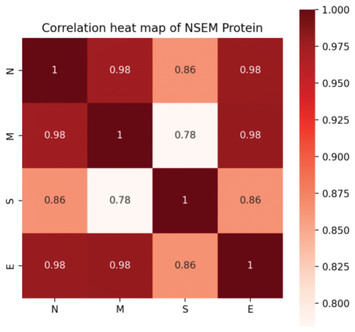
The evolution of SARS-CoV-2 and the COVID-19 pandemic
"The study provides valuable insights into the worldwide endeavors in preventing epidemics and conducting scientific research on the evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It extensively examines the binding ability prediction and mutation rates of SARS-CoV-2, highlighting the adaptive relationship between humans and the virus. The findings derived from this comprehensive meta-analysis offer significant insights that can aid in the development of effective long-term strategies to combat human pathogens."
 Mariella Pazzaglia, Handling Editor
Mariella Pazzaglia, Handling Editor
 Mariella Pazzaglia, Handling Editor
Mariella Pazzaglia, Handling Editor
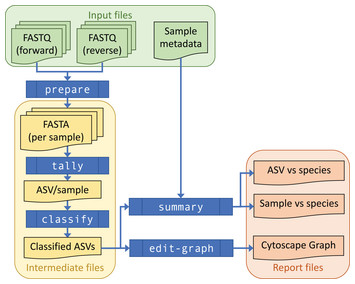
18 August 2023
THAPBI PICT—a fast, cautious, and accurate metabarcoding analysis pipeline
"This study presents a novel and flexible pipeline for the objective analysis of metabarcode data, with user-friendly reports including Amplicon Sequence Variants read counts enabling custom graphs, as well as summary species lists per sample."
 Xavier Pochon, Handling Editor
Xavier Pochon, Handling Editor
 Xavier Pochon, Handling Editor
Xavier Pochon, Handling Editor
17 August 2023
Curcumin Chalcone Derivatives Database (CCDD): a Python framework for natural compound derivatives database
"Good one"
 Nagarajan Raju, Handling Editor
Nagarajan Raju, Handling Editor
 Nagarajan Raju, Handling Editor
Nagarajan Raju, Handling Editor
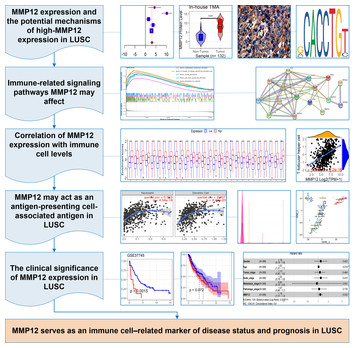
16 August 2023
MMP12 serves as an immune cell–related marker of disease status and prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
"The article titled "MMP12 serves as an immune cell–related marker of disease status and prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma" is of significant importance in the field of lung cancer research. This study explores the role of MMP12 as a potential marker for disease status and prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications.
The identification of reliable markers for disease monitoring and prognostic assessment is crucial for improving patient outcomes. By investigating the role of MMP12, the authors provide valuable insights into the intricate interplay between immune cells and cancer progression in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Such knowledge can aid in the development of targeted therapies and personalized treatment strategies.
Furthermore, lung squamous cell carcinoma represents a significant healthcare burden globally. This study's findings have the potential to contribute to early detection, accurate disease monitoring, and prognostic stratification, ultimately improving patient management and survival rates. The impact of this research extends beyond the academic realm, holding promise for clinical applications and positively influencing the field of lung cancer research.
Overall, the article addresses an important research gap and provides novel insights into the role of MMP12 as a disease status and prognostic marker in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Its publication will undoubtedly contribute to the existing body of knowledge and stimulate further investigations in this area, ultimately benefiting both researchers and clinicians in the fight against lung cancer."
 Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
 Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
Mahesh Gokara, Handling Editor
55,958 Followers