PeerJ Section
Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 6 (view impact metrics).
55,038 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology articles 
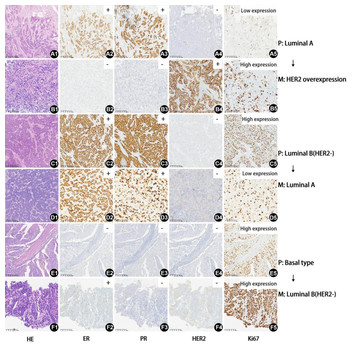
15 May 2024
Retrospective analysis of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), Ki67 changes and their clinical significance between primary breast cancer and metastatic tumors
"In this retrospective analysis, the authors find differences in the expression of relevant breast cancer receptors (ER, PR, HER2, and Ki67) between primary and metastasis tumors in Chinese women. This finding is applicable in the biopsy context and in the following of breast cancer patients."
 Tanya Camacho-Villegas, Handling Editor
Tanya Camacho-Villegas, Handling Editor
 Tanya Camacho-Villegas, Handling Editor
Tanya Camacho-Villegas, Handling Editor

14 May 2024
Hsa_circ_0009096/miR-370-3p modulates hepatic stellate cell proliferation and fibrosis during biliary atresia pathogenesis
"This work is crucial for unraveling the novel functions of circular RNA 0009096 (Hsa_circ_0009096) in hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and its potential implications in biliary atresia (BA) pathogenesis. By establishing the relevance of the in vitro HSC model to BA, elucidating Hsa_circ_0009096 expression in normal and BA liver samples, and identifying specific miRNA interactions, the study aims to provide essential insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying BA development. Validating gene expression at the protein level and refining experimental design contribute to the study's scientific rigor, enhancing its potential impact on diagnosis and treatment strategies for BA."
 Himanshu Singh, Handling Editor
Himanshu Singh, Handling Editor
 Himanshu Singh, Handling Editor
Himanshu Singh, Handling Editor

14 May 2024
A comprehensive analysis of the oncogenic and prognostic role of TBC1Ds in human hepatocellular carcinoma
"Overall, this research offers a novel perspective and draws meaningful conclusions. The authors' use of a series of cell function assays to support their arguments enhances the credibility of the research findings. The study is well-designed, rigorously analyzed, and thoroughly argued, making it a valuable contribution to our understanding of the role of the TBC1D family in the development and progression of liver cancer. This article is worthy of reference and inspiration for researchers in the field of hepatocellular carcinoma."
 Jincheng Wang, Handling Editor
Jincheng Wang, Handling Editor
 Jincheng Wang, Handling Editor
Jincheng Wang, Handling Editor
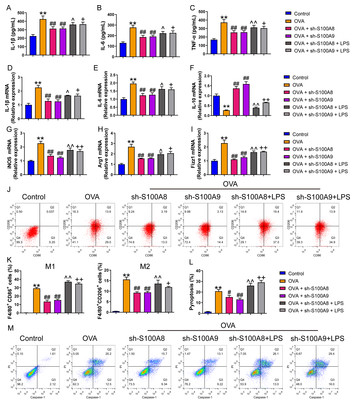
18 April 2024
S100A8/9 modulates perturbation and glycolysis of macrophages in allergic asthma mice
"This research investigates the role of S100A8 and S100A9 molecules in allergic asthma, highlighting their impact on macrophage behavior and glycolysis through the (likely) TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. The study demonstrates that S100A8 and S100A9 promote inflammatory responses, macrophage polarization, and glycolysis, contributing to asthma pathogenesis. Conversely, inhibiting these molecules shows promising therapeutic potential, as evidenced by improved respiratory function and reduced inflammation in mouse models. These findings offer valuable insights into the immune dysregulation and metabolic alterations associated with allergic asthma, suggesting new avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions to alleviate asthma symptoms and improve patient outcomes."
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
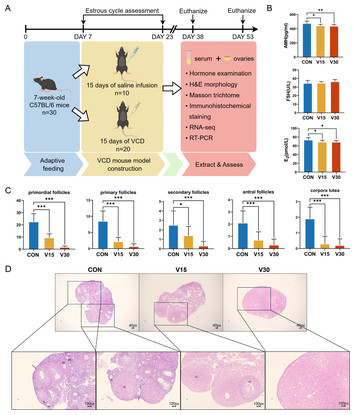
18 April 2024
Transcriptome analysis during 4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide exposure-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in mice
"If VCD is used in a poorly ventilated workspace, it could be inhaled as dust or vapor. or via skin by Direct contact with VCD through contaminated clothing or surfaces. this work It confirms previous findings of VCD's impact on ovarian function, Shows potential differences in damage depending on the duration of exposure (day 15 vs day 30), Identifies potential mechanisms like steroid hormone synthesis and DNA repair as areas for future research on treatment strategies. VCD-induced POI specifically reduces the number of eggs available for ovulation, impacting fertility. this work sheds light on a specific environmental risk factor for POI and potentially offers clues for future research on POI mechanisms."
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
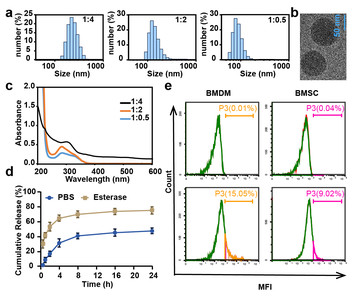
9 April 2024
The role of echinacoside-based cross-linker nanoparticles in the treatment of osteoporosis
"This study on the therapeutic effects of cross-linker (CL)-ECH nanoparticles in treating osteoporosis is important due to several key reasons. Firstly, the current drugs used for osteoporosis treatment often come with toxic side effects, highlighting the urgent need for safer and more effective alternatives. The utilization of Echinacoside (ECH) as a natural small molecule drug and the development of CL-ECH nanoparticles present a novel and promising approach to address this issue. The research exploring the antioxidant effects of CL-ECH nanoparticles on bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and their impact on bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying osteoporosis treatment. The findings of this study, particularly the suppression of oxidative stress in BMDMs and the improvement in bone trabecular loss in an ovariectomized mouse model, demonstrate the potential of CL-ECH nanoparticles as a more targeted and efficient therapeutic intervention for osteoporosis. Furthermore, the identification of NRF-2 nuclear translocation as a key pathway affected by CL-ECH nanoparticles, leading to the downregulation of NF-κB expression and inhibition of osteoclast production, contributes significantly to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in bone resorption and osteoporosis progression. These insights have the potential to inform the development of a new generation of anti-bone resorption drugs with enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects. This article not only offers a promising alternative for osteoporosis treatment but also advances our knowledge of the pathophysiology of the disease. The potential impact of this research on the field lies in its contribution to the development of safer and more targeted therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis, ultimately benefitting patients by improving treatment outcomes and quality of life."
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
 Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
Fanglin Guan, Handling Editor
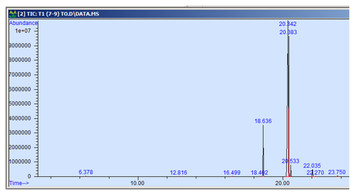
29 March 2024
Identification, validation and quantification of thymoquinone in conjunction with assessment of bioactive possessions and GC-MS profiling of pharmaceutically valuable crop Nigella (Nigella sativa L.) varieties
 Anshuman Singh, Handling Editor
Anshuman Singh, Handling Editor
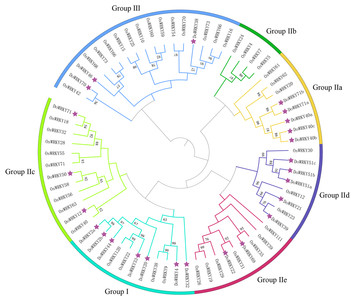
28 March 2024
Identification of WRKY gene family in Dioscorea opposita Thunb. reveals that DoWRKY71 enhanced the tolerance to cold and ABA stress
"This is good piece of work and will enhance about our knowledge about the WRKY family and their role in abiotic stress tolerance."
 Kashmir Singh, Handling Editor
Kashmir Singh, Handling Editor
 Kashmir Singh, Handling Editor
Kashmir Singh, Handling Editor
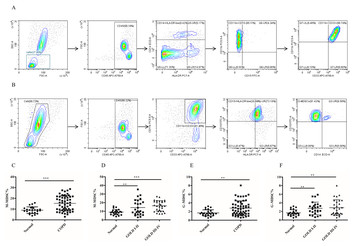
27 March 2024
The clinical association of programmed death-1/PD-L1 axis, myeloid derived suppressor cells subsets and regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of stable COPD patients
 Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
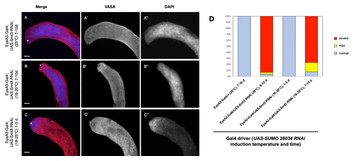
14 March 2024
Chigno/CG11180 and SUMO are Chinmo-interacting proteins with a role in Drosophila testes somatic support cells
"This paper identifies new players in Drosphila testes stem cell differentiation by identifying Chimno interacting partners."
 Judith Yanowitz, Handling Editor
Judith Yanowitz, Handling Editor
 Judith Yanowitz, Handling Editor
Judith Yanowitz, Handling Editor
Collections
View all 
Biological Clocks and Social Organization

PeerJ at 10 - our first 30 papers.

Advances in Illuminating the Druggable Genome
Food Safety Issues During- and Post-Pandemic/Epidemic Situations; Production, Packaging, Storage, and Analysis Interventions

Pulsed Resources Impacts on Biological Processes: From Genes to Ecosystems

55,038 Followers


